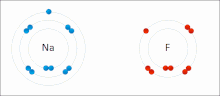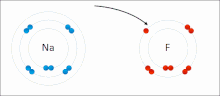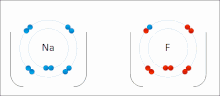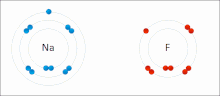
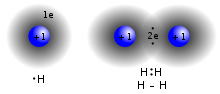
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, or between two atoms with sharply...
18 KB (2,338 words) - 02:36, 8 February 2024
ionic and metallic bonds, and "weak bonds" or "secondary bonds" such as dipole–dipole interactions, the London dispersion force, and hydrogen bonding...
40 KB (4,872 words) - 13:33, 22 September 2024
covalent bonding is much more common than ionic bonding. Covalent bonding also includes many kinds of interactions, including σ-bonding, π-bonding, metal-to-metal...
28 KB (3,673 words) - 14:01, 24 October 2024
Intramolecular force (category Chemical bonding)
bonds — ionic, covalent, and metallic — distinguished by the degree of charge separation between participating atoms. The characteristics of the bond formed...
7 KB (795 words) - 21:19, 6 November 2024
bonded compounds. In ionic compounds, the electronegativity of the two atoms bonding together has a major effect on their bond energy. The extent of...
9 KB (1,318 words) - 02:44, 29 April 2024
Kazimierz Fajans in 1923, are used to predict whether a chemical bond will be covalent or ionic, and depend on the charge on the cation and the relative sizes...
5 KB (534 words) - 01:02, 6 June 2024
Salt (chemistry) (redirect from Ionic salt)
between the charge distribution of these bodies, and in particular, the ionic bond resulting from the long-ranged Coulomb attraction between the net negative...
63 KB (6,942 words) - 00:48, 22 October 2024
Chemical polarity (redirect from Polar bond)
of 1.7 corresponds to 50% ionic character, so that a greater difference corresponds to a bond which is predominantly ionic. As a quantum-mechanical description...
24 KB (2,751 words) - 02:20, 28 September 2024