In chemistry, a lyonium ion is the cation derived by the protonation of a solvent molecule. For example, a hydronium ion is formed by the protonation of...
1,008 bytes (98 words) - 12:28, 18 July 2023
methanol. Its counterpart is a lyonium ion, the cation formed by the protonation of a solvent molecule. Lyonium and lyate ions, resulting from molecular autoionization...
1,016 bytes (93 words) - 12:28, 18 July 2023
ethynium, C2H+3 (protonated ethyne) Carbonium ion Lyonium ion, a protonated solvent molecule Lyate ion, a deprotonated solvent molecule Onium compounds...
16 KB (1,499 words) - 15:22, 4 December 2023
PH (redirect from Hydrogen-ion concentration)
proton ions, such as lyonium ions, which require an intersolvent scale which involves the transfer activity coefficient of hydronium/lyonium ion. pH is...
52 KB (6,447 words) - 18:59, 30 October 2024
solvo-acids; when protonated solvent, they are lyonium ions. solvate ions: a generic name for negative ions. These are also sometimes called solve-bases;...
36 KB (4,969 words) - 08:10, 10 September 2024
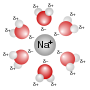
classic example is when water molecules arrange around a metal ion. If the metal ion is a cation, the electronegative oxygen atom of the water molecule...
5 KB (642 words) - 09:58, 7 January 2024
Hydration number (section Using Ion movement methods)
compound is defined as the number of molecules of water bonded to a central ion, often a metal cation. The hydration number is related to the broader concept...
9 KB (1,071 words) - 01:32, 8 July 2023
particular lyonium ions and lyate ions generated by molecular autoionization of protic and aprotic solvents due to Grotthuss mechanism of ion hopping depending...
5 KB (894 words) - 16:55, 3 May 2021