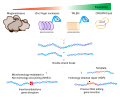
pigmentosum, complementation group C, also known as XPC, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the XPC gene. XPC is involved in the recognition of bulky DNA...
16 KB (1,923 words) - 21:51, 26 November 2023
Xeroderma pigmentosum, complementation group C, a human gene xPC Target, a product from MathWorks XPC Golf Clubs, a proprietary brand from Golfsmith This...
454 bytes (88 words) - 07:36, 15 March 2013
cancer types. The XPC gene is responsible for a protein which recognizes DNA during the early portion of the NER pathway. This gene can have polymorphisms...
33 KB (3,623 words) - 18:02, 20 August 2024
Genome editing (redirect from Human gene editing therapy)
industrial-scale production of two meganucleases able to cleave the human XPC gene; mutations in this gene result in Xeroderma pigmentosum, a severe monogenic disorder...
78 KB (9,361 words) - 01:20, 25 September 2024
I-CreI derivatives cleaving sequences from the human XPC gene can induce highly efficient gene correction in mammalian cells". Journal of Molecular Biology...
20 KB (2,295 words) - 10:15, 4 July 2022
Antimutagen (section Tumor suppressor genes)
break repair by rejoining and induction of genes related to base and nucleotide excision repair such as XPA and XPC; Selenium: Induces programmed cell death...
8 KB (1,032 words) - 23:26, 3 November 2023
H3, and H4, as well as the repair protein XPC, which has been attracted to the site of the DNA damage. XPC, upon ubiquitination, is activated and initiates...
81 KB (10,099 words) - 11:45, 3 September 2024
RAD23B (redirect from RAD23B (gene))
cells. The complex of XPC-RAD23B is the initial damage recognition factor in global genomic nucleotide excision repair (GG-NER). XPC-RAD23B recognizes a...
15 KB (1,848 words) - 23:42, 12 September 2024
Carcinogenesis (section Tumor suppressor genes)
Wickliffe J, Salazar J, Boldogh I, Xie J (October 2015). "Genetic Evidence for XPC-KRAS Interactions During Lung Cancer Development". Journal of Genetics and...
115 KB (13,952 words) - 04:56, 2 November 2024
pigmentosum may be caused by genetic mutations in 8 genes, which produce the following enzymes: XPA, XPB, XPC, XPD, XPE, XPF, XPG and Pol η. XPA-XPF are nucleotide...
51 KB (5,582 words) - 14:19, 15 July 2024