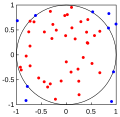
In computing, a Monte Carlo algorithm is a randomized algorithm whose output may be incorrect with a certain (typically small) probability. Two examples...
11 KB (1,185 words) - 07:36, 25 June 2024
In statistics, Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) is a class of algorithms used to draw samples from a probability distribution. Given a probability distribution...
29 KB (3,062 words) - 20:03, 13 June 2024
computes a definite integral. While other algorithms usually evaluate the integrand at a regular grid, Monte Carlo randomly chooses points at which the integrand...
18 KB (2,519 words) - 09:52, 12 June 2024
Monte Carlo methods, or Monte Carlo experiments, are a broad class of computational algorithms that rely on repeated random sampling to obtain numerical...
85 KB (9,795 words) - 10:52, 21 June 2024
statistics and statistical physics, the Metropolis–Hastings algorithm is a Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) method for obtaining a sequence of random samples...
30 KB (4,535 words) - 20:02, 13 June 2024
(Las Vegas algorithms, for example Quicksort), and algorithms which have a chance of producing an incorrect result (Monte Carlo algorithms, for example...
32 KB (4,173 words) - 21:10, 30 March 2024
contrast to Monte Carlo algorithms, the Las Vegas algorithm can guarantee the correctness of any reported result. // Las Vegas algorithm repeat: k = RandInt(n)...
17 KB (2,504 words) - 04:33, 12 June 2024
The Hamiltonian Monte Carlo algorithm (originally known as hybrid Monte Carlo) is a Markov chain Monte Carlo method for obtaining a sequence of random...
13 KB (2,127 words) - 17:39, 26 June 2024
In computer science, Monte Carlo tree search (MCTS) is a heuristic search algorithm for some kinds of decision processes, most notably those employed in...
39 KB (4,697 words) - 16:25, 5 July 2024
properties and numerically exact exponentially scaling quantum Monte Carlo algorithms, but none that are both. In principle, any physical system can be...
9 KB (1,140 words) - 19:56, 21 September 2022