Enzymes (/ˈɛnzaɪmz/) are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called...
96 KB (9,821 words) - 16:54, 27 October 2024
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for...
104 KB (11,579 words) - 19:29, 18 September 2024
Enzyme kinetics is the study of the rates of enzyme-catalysed chemical reactions. In enzyme kinetics, the reaction rate is measured and the effects of...
71 KB (9,341 words) - 03:06, 26 August 2024
A restriction enzyme, restriction endonuclease, REase, ENase or restrictase is an enzyme that cleaves DNA into fragments at or near specific recognition...
55 KB (5,853 words) - 14:21, 27 September 2024
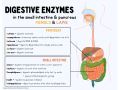
Digestive enzymes take part in the chemical process of digestion, which follows the mechanical process of digestion. Food consists of macromolecules of...
18 KB (2,239 words) - 09:27, 1 August 2024
Enzyme catalysis is the increase in the rate of a process by an "enzyme", a biological molecule. Most enzymes are proteins, and most such processes are...
43 KB (5,001 words) - 18:45, 7 August 2024
The Enzyme Commission number (EC number) is a numerical classification scheme for enzymes, based on the chemical reactions they catalyze. As a system...
10 KB (895 words) - 11:45, 9 July 2024
The enzyme unit, or international unit for enzyme (symbol U, sometimes also IU) is a unit of enzyme's catalytic activity. 1 U (μmol/min) is defined as...
3 KB (397 words) - 02:47, 20 April 2024
Industrial enzymes are enzymes that are commercially used in a variety of industries such as pharmaceuticals, chemical production, biofuels, food and...
15 KB (1,580 words) - 20:41, 27 August 2024
Cofactor (biochemistry) (redirect from Co-enzyme)
non-protein chemical compound or metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's role as a catalyst (a catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of...
48 KB (4,931 words) - 20:58, 10 November 2024