The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of Lentivirus (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency...
123 KB (14,115 words) - 13:33, 14 October 2024
immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. It is a preventable disease. There is no vaccine or cure for HIV. It can be managed...
211 KB (21,173 words) - 15:29, 13 November 2024
HIV tests are used to detect the presence of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the virus that causes HIV/AIDS, in serum, saliva, or urine. Such tests...
46 KB (5,753 words) - 19:05, 3 September 2024
The global pandemic of HIV/AIDS (human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) began in 1981, and is an ongoing worldwide...
88 KB (8,612 words) - 14:14, 7 November 2024
In Western Europe, the routes of transmission of HIV are diverse, including paid sex, sex between men, intravenous drugs, mother to child transmission...
38 KB (4,179 words) - 07:12, 14 July 2024
HIV/AIDS denialism is the belief, despite conclusive evidence to the contrary, that the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) does not cause acquired immune...
93 KB (10,106 words) - 21:36, 23 September 2024
The subtypes of HIV include two main subtypes, known as HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). These subtypes have distinct genetic differences and...
34 KB (3,864 words) - 22:49, 7 November 2024
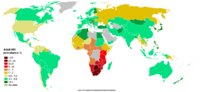
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which causes AIDS, varies in prevalence from nation to nation. Listed here are the prevalence rates among adults...
27 KB (916 words) - 13:07, 14 October 2024
are two types of HIV: HIV-1 and HIV-2. HIV-1 is more virulent, more easily transmitted, and it is the cause of the vast majority of HIV infections globally...
118 KB (14,015 words) - 21:49, 13 November 2024
HIV superinfection (also called HIV reinfection or SuperAIDS) is a condition in which a person with an established human immunodeficiency virus infection...
25 KB (3,119 words) - 21:04, 14 July 2024