Formulation of classical mechanics using momenta
Sir William Rowan Hamilton In physics , Hamiltonian mechanics is a reformulation of Lagrangian mechanics that emerged in 1833. Introduced by Sir William Rowan Hamilton ,[ 1] q ˙ i {\displaystyle {\dot {q}}^{i}} momenta . Both theories provide interpretations of classical mechanics and describe the same physical phenomena.
Hamiltonian mechanics has a close relationship with geometry (notably, symplectic geometry and Poisson structures ) and serves as a link between classical and quantum mechanics .
p , q ) and Hamiltonian H [ edit ] Let ( M , L ) {\displaystyle (M,{\mathcal {L}})} mechanical system with configuration space M {\displaystyle M} Lagrangian L . {\displaystyle {\mathcal {L}}.} ( q , q ˙ ) {\displaystyle ({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})} M . {\displaystyle M.} p i ( q , q ˙ , t ) = def ∂ L / ∂ q ˙ i {\displaystyle \textstyle p_{i}({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)~{\stackrel {\text{def}}{=}}~{\partial {\mathcal {L}}}/{\partial {\dot {q}}^{i}}} momenta . (Also generalized momenta , conjugate momenta , and canonical momenta ). For a time instant t , {\displaystyle t,} Legendre transformation of L {\displaystyle {\mathcal {L}}} ( q , q ˙ ) → ( p , q ) {\displaystyle ({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})\to \left({\boldsymbol {p}},{\boldsymbol {q}}\right)} ( p , q ) → ( q , q ˙ ) . {\displaystyle ({\boldsymbol {p}},{\boldsymbol {q}})\to ({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}}).} n {\displaystyle n} energy function E L ( q , q ˙ , t ) = def ∑ i = 1 n q ˙ i ∂ L ∂ q ˙ i − L . {\displaystyle E_{\mathcal {L}}({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)\,{\stackrel {\text{def}}{=}}\,\sum _{i=1}^{n}{\dot {q}}^{i}{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial {\dot {q}}^{i}}}-{\mathcal {L}}.}
The Legendre transform of L {\displaystyle {\mathcal {L}}} E L {\displaystyle E_{\mathcal {L}}} H ( p , q , t ) {\displaystyle {\mathcal {H}}({\boldsymbol {p}},{\boldsymbol {q}},t)} Hamiltonian . The Hamiltonian satisfies H ( ∂ L ∂ q ˙ , q , t ) = E L ( q , q ˙ , t ) {\displaystyle {\mathcal {H}}\left({\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial {\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}}}},{\boldsymbol {q}},t\right)=E_{\mathcal {L}}({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)} H ( p , q , t ) = ∑ i = 1 n p i q ˙ i − L ( q , q ˙ , t ) , {\displaystyle {\mathcal {H}}({\boldsymbol {p}},{\boldsymbol {q}},t)=\sum _{i=1}^{n}p_{i}{\dot {q}}^{i}-{\mathcal {L}}({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t),} q ˙ = ( q ˙ 1 , … , q ˙ n ) {\displaystyle {\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}}=({\dot {q}}^{1},\ldots ,{\dot {q}}^{n})} n {\displaystyle n} p = ∂ L / ∂ q ˙ {\displaystyle \textstyle {\boldsymbol {p}}={\partial {\mathcal {L}}}/{\partial {\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}}}} q ˙ {\displaystyle {\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}}} . The ( 2 n {\displaystyle 2n} ( p , q ) {\displaystyle ({\boldsymbol {p}},{\boldsymbol {q}})} phase space coordinates . (Also canonical coordinates ).
[ edit ] In phase space coordinates ( p , q ) {\displaystyle ({\boldsymbol {p}},{\boldsymbol {q}})} , the ( n {\displaystyle n} Euler–Lagrange equation ∂ L ∂ q − d d t ∂ L ∂ q ˙ = 0 {\displaystyle {\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial {\boldsymbol {q}}}}-{\frac {d}{dt}}{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial {\dot {\boldsymbol {q}}}}}=0} Hamilton's equations in 2 n {\displaystyle 2n}
d q d t = ∂ H ∂ p , d p d t = − ∂ H ∂ q . {\displaystyle {\frac {\mathrm {d} {\boldsymbol {q}}}{\mathrm {d} t}}={\frac {\partial {\mathcal {H}}}{\partial {\boldsymbol {p}}}},\quad {\frac {\mathrm {d} {\boldsymbol {p}}}{\mathrm {d} t}}=-{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {H}}}{\partial {\boldsymbol {q}}}}.}
Proof The Hamiltonian H ( p , q ) {\displaystyle {\mathcal {H}}({\boldsymbol {p}},{\boldsymbol {q}})} Legendre transform of the Lagrangian L ( q , q ˙ ) {\displaystyle {\mathcal {L}}({\boldsymbol {q}},{\dot {\boldsymbol {q}}})} L ( q , q ˙ ) + H ( p , q ) = p q ˙ {\displaystyle {\mathcal {L}}({\boldsymbol {q}},{\dot {\boldsymbol {q}}})+{\mathcal {H}}({\boldsymbol {p}},{\boldsymbol {q}})={\boldsymbol {p}}{\dot {\boldsymbol {q}}}} ∂ H ∂ p = q ˙ ∂ L ∂ q = − ∂ H ∂ q , {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {H}}}{\partial {\boldsymbol {p}}}}&={\dot {\boldsymbol {q}}}\\{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial {\boldsymbol {q}}}}&=-{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {H}}}{\partial {\boldsymbol {q}}}},\end{aligned}}}
Besides, since p = ∂ L / ∂ q ˙ {\displaystyle {\boldsymbol {p}}=\partial {\mathcal {L}}/\partial {\dot {\boldsymbol {q}}}} p ˙ = d p d t = ∂ L ∂ q = − ∂ H ∂ q . {\displaystyle {\dot {\boldsymbol {p}}}={\frac {\mathrm {d} {\boldsymbol {p}}}{\mathrm {d} t}}={\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial {\boldsymbol {q}}}}=-{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {H}}}{\partial {\boldsymbol {q}}}}.}
[ edit ] Let P ( a , b , x a , x b ) {\displaystyle {\mathcal {P}}(a,b,{\boldsymbol {x}}_{a},{\boldsymbol {x}}_{b})} q : [ a , b ] → M {\displaystyle {\boldsymbol {q}}:[a,b]\to M} q ( a ) = x a {\displaystyle {\boldsymbol {q}}(a)={\boldsymbol {x}}_{a}} q ( b ) = x b . {\displaystyle {\boldsymbol {q}}(b)={\boldsymbol {x}}_{b}.} action functional S : P ( a , b , x a , x b ) → R {\displaystyle {\mathcal {S}}:{\mathcal {P}}(a,b,{\boldsymbol {x}}_{a},{\boldsymbol {x}}_{b})\to \mathbb {R} } S [ q ] = ∫ a b L ( t , q ( t ) , q ˙ ( t ) ) d t = ∫ a b ( ∑ i = 1 n p i q ˙ i − H ( p , q , t ) ) d t , {\displaystyle {\mathcal {S}}[{\boldsymbol {q}}]=\int _{a}^{b}{\mathcal {L}}(t,{\boldsymbol {q}}(t),{\dot {\boldsymbol {q}}}(t))\,dt=\int _{a}^{b}\left(\sum _{i=1}^{n}p_{i}{\dot {q}}^{i}-{\mathcal {H}}({\boldsymbol {p}},{\boldsymbol {q}},t)\right)\,dt,} q = q ( t ) {\displaystyle {\boldsymbol {q}}={\boldsymbol {q}}(t)} , and p = ∂ L / ∂ q ˙ {\displaystyle {\boldsymbol {p}}=\partial {\mathcal {L}}/\partial {\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}}} q ∈ P ( a , b , x a , x b ) {\displaystyle {\boldsymbol {q}}\in {\mathcal {P}}(a,b,{\boldsymbol {x}}_{a},{\boldsymbol {x}}_{b})} stationary point of S {\displaystyle {\mathcal {S}}} ( p ( t ) , q ( t ) ) {\displaystyle ({\boldsymbol {p}}(t),{\boldsymbol {q}}(t))}
Basic physical interpretation [ edit ] A simple interpretation of Hamiltonian mechanics comes from its application on a one-dimensional system consisting of one nonrelativistic particle of mass m . The value H ( p , q ) {\displaystyle H(p,q)} kinetic and potential energy , traditionally denoted T and V , respectively. Here p is the momentum mv and q is the space coordinate. Then H = T + V , T = p 2 2 m , V = V ( q ) {\displaystyle {\mathcal {H}}=T+V,\qquad T={\frac {p^{2}}{2m}},\qquad V=V(q)} T is a function of p alone, while V is a function of q alone (i.e., T and V are scleronomic ).
In this example, the time derivative of q is the velocity, and so the first Hamilton equation means that the particle's velocity equals the derivative of its kinetic energy with respect to its momentum. The time derivative of the momentum p equals the Newtonian force , and so the second Hamilton equation means that the force equals the negative gradient of potential energy.
A spherical pendulum consists of a mass m moving without friction on the surface of a sphere . The only forces acting on the mass are the reaction from the sphere and gravity . Spherical coordinates are used to describe the position of the mass in terms of (r , θ , φ ) , where r r = ℓ
Spherical pendulum : angles and velocities.The Lagrangian for this system is[ 2] L = 1 2 m ℓ 2 ( θ ˙ 2 + sin 2 θ φ ˙ 2 ) + m g ℓ cos θ . {\displaystyle L={\frac {1}{2}}m\ell ^{2}\left({\dot {\theta }}^{2}+\sin ^{2}\theta \ {\dot {\varphi }}^{2}\right)+mg\ell \cos \theta .}
Thus the Hamiltonian is H = P θ θ ˙ + P φ φ ˙ − L {\displaystyle H=P_{\theta }{\dot {\theta }}+P_{\varphi }{\dot {\varphi }}-L} P θ = ∂ L ∂ θ ˙ = m ℓ 2 θ ˙ {\displaystyle P_{\theta }={\frac {\partial L}{\partial {\dot {\theta }}}}=m\ell ^{2}{\dot {\theta }}} P φ = ∂ L ∂ φ ˙ = m ℓ 2 sin 2 θ φ ˙ . {\displaystyle P_{\varphi }={\frac {\partial L}{\partial {\dot {\varphi }}}}=m\ell ^{2}\sin ^{2}\!\theta \,{\dot {\varphi }}.} H = [ 1 2 m ℓ 2 θ ˙ 2 + 1 2 m ℓ 2 sin 2 θ φ ˙ 2 ] ⏟ T + [ − m g ℓ cos θ ] ⏟ V = P θ 2 2 m ℓ 2 + P φ 2 2 m ℓ 2 sin 2 θ − m g ℓ cos θ . {\displaystyle H=\underbrace {\left[{\frac {1}{2}}m\ell ^{2}{\dot {\theta }}^{2}+{\frac {1}{2}}m\ell ^{2}\sin ^{2}\!\theta \,{\dot {\varphi }}^{2}\right]} _{T}+\underbrace {{\Big [}-mg\ell \cos \theta {\Big ]}} _{V}={\frac {P_{\theta }^{2}}{2m\ell ^{2}}}+{\frac {P_{\varphi }^{2}}{2m\ell ^{2}\sin ^{2}\theta }}-mg\ell \cos \theta .} θ ˙ = P θ m ℓ 2 φ ˙ = P φ m ℓ 2 sin 2 θ P θ ˙ = P φ 2 m ℓ 2 sin 3 θ cos θ − m g ℓ sin θ P φ ˙ = 0. {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\dot {\theta }}&={P_{\theta } \over m\ell ^{2}}\\[6pt]{\dot {\varphi }}&={P_{\varphi } \over m\ell ^{2}\sin ^{2}\theta }\\[6pt]{\dot {P_{\theta }}}&={P_{\varphi }^{2} \over m\ell ^{2}\sin ^{3}\theta }\cos \theta -mg\ell \sin \theta \\[6pt]{\dot {P_{\varphi }}}&=0.\end{aligned}}} P φ {\displaystyle P_{\varphi }} , which corresponds to the vertical component of angular momentum L z = ℓ sin θ × m ℓ sin θ φ ˙ {\displaystyle L_{z}=\ell \sin \theta \times m\ell \sin \theta \,{\dot {\varphi }}} , is a constant of motion. That is a consequence of the rotational symmetry of the system around the vertical axis. Being absent from the Hamiltonian, azimuth φ {\displaystyle \varphi } cyclic coordinate , which implies conservation of its conjugate momentum.
[ edit ] Hamilton's equations can be derived by a calculation with the Lagrangian L {\displaystyle {\mathcal {L}}} , generalized positions qi , and generalized velocities ⋅ q i i = 1 , … , n {\displaystyle i=1,\ldots ,n} .[ 3] off-shell , meaning q i {\displaystyle q^{i}} , q ˙ i {\displaystyle {\dot {q}}^{i}} , t {\displaystyle t} are independent coordinates in phase space, not constrained to follow any equations of motion (in particular, q ˙ i {\displaystyle {\dot {q}}^{i}} q i {\displaystyle q^{i}} ). The total differential of the Lagrangian is: d L = ∑ i ( ∂ L ∂ q i d q i + ∂ L ∂ q ˙ i d q ˙ i ) + ∂ L ∂ t d t . {\displaystyle \mathrm {d} {\mathcal {L}}=\sum _{i}\left({\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial q^{i}}}\mathrm {d} q^{i}+{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial {\dot {q}}^{i}}}\,\mathrm {d} {\dot {q}}^{i}\right)+{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial t}}\,\mathrm {d} t\ .} p i = ∂ L / ∂ q ˙ i {\displaystyle p_{i}=\partial {\mathcal {L}}/\partial {\dot {q}}^{i}} , so we may rewrite the equation as: d L = ∑ i ( ∂ L ∂ q i d q i + p i d q ˙ i ) + ∂ L ∂ t d t = ∑ i ( ∂ L ∂ q i d q i + d ( p i q ˙ i ) − q ˙ i d p i ) + ∂ L ∂ t d t . {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\mathrm {d} {\mathcal {L}}=&\sum _{i}\left({\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial q^{i}}}\,\mathrm {d} q^{i}+p_{i}\mathrm {d} {\dot {q}}^{i}\right)+{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial t}}\mathrm {d} t\\=&\sum _{i}\left({\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial q^{i}}}\,\mathrm {d} q^{i}+\mathrm {d} (p_{i}{\dot {q}}^{i})-{\dot {q}}^{i}\,\mathrm {d} p_{i}\right)+{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial t}}\,\mathrm {d} t\,.\end{aligned}}}
After rearranging, one obtains: d ( ∑ i p i q ˙ i − L ) = ∑ i ( − ∂ L ∂ q i d q i + q ˙ i d p i ) − ∂ L ∂ t d t . {\displaystyle \mathrm {d} \!\left(\sum _{i}p_{i}{\dot {q}}^{i}-{\mathcal {L}}\right)=\sum _{i}\left(-{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial q^{i}}}\,\mathrm {d} q^{i}+{\dot {q}}^{i}\mathrm {d} p_{i}\right)-{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial t}}\,\mathrm {d} t\ .}
The term in parentheses on the left-hand side is just the Hamiltonian H = ∑ p i q ˙ i − L {\textstyle {\mathcal {H}}=\sum p_{i}{\dot {q}}^{i}-{\mathcal {L}}} d H = ∑ i ( − ∂ L ∂ q i d q i + q ˙ i d p i ) − ∂ L ∂ t d t . {\displaystyle \mathrm {d} {\mathcal {H}}=\sum _{i}\left(-{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial q^{i}}}\,\mathrm {d} q^{i}+{\dot {q}}^{i}\,\mathrm {d} p_{i}\right)-{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial t}}\,\mathrm {d} t\ .}
One may also calculate the total differential of the Hamiltonian H {\displaystyle {\mathcal {H}}} q i {\displaystyle q^{i}} , p i {\displaystyle p_{i}} , t {\displaystyle t} instead of q i {\displaystyle q^{i}} , q ˙ i {\displaystyle {\dot {q}}^{i}} , t {\displaystyle t} , yielding: d H = ∑ i ( ∂ H ∂ q i d q i + ∂ H ∂ p i d p i ) + ∂ H ∂ t d t . {\displaystyle \mathrm {d} {\mathcal {H}}=\sum _{i}\left({\frac {\partial {\mathcal {H}}}{\partial q^{i}}}\mathrm {d} q^{i}+{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {H}}}{\partial p_{i}}}\mathrm {d} p_{i}\right)+{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {H}}}{\partial t}}\,\mathrm {d} t\ .}
One may now equate these two expressions for d H {\displaystyle d{\mathcal {H}}} , one in terms of L {\displaystyle {\mathcal {L}}} , the other in terms of H {\displaystyle {\mathcal {H}}} : ∑ i ( − ∂ L ∂ q i d q i + q ˙ i d p i ) − ∂ L ∂ t d t = ∑ i ( ∂ H ∂ q i d q i + ∂ H ∂ p i d p i ) + ∂ H ∂ t d t . {\displaystyle \sum _{i}\left(-{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial q^{i}}}\mathrm {d} q^{i}+{\dot {q}}^{i}\mathrm {d} p_{i}\right)-{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial t}}\,\mathrm {d} t\ =\ \sum _{i}\left({\frac {\partial {\mathcal {H}}}{\partial q^{i}}}\mathrm {d} q^{i}+{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {H}}}{\partial p_{i}}}\mathrm {d} p_{i}\right)+{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {H}}}{\partial t}}\,\mathrm {d} t\ .}
Since these calculations are off-shell, one can equate the respective coefficients of d q i {\displaystyle \mathrm {d} q^{i}} , d p i {\displaystyle \mathrm {d} p_{i}} , d t {\displaystyle \mathrm {d} t} on the two sides: ∂ H ∂ q i = − ∂ L ∂ q i , ∂ H ∂ p i = q ˙ i , ∂ H ∂ t = − ∂ L ∂ t . {\displaystyle {\frac {\partial {\mathcal {H}}}{\partial q^{i}}}=-{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial q^{i}}}\quad ,\quad {\frac {\partial {\mathcal {H}}}{\partial p_{i}}}={\dot {q}}^{i}\quad ,\quad {\frac {\partial {\mathcal {H}}}{\partial t}}=-{\partial {\mathcal {L}} \over \partial t}\ .}
On-shell, one substitutes parametric functions q i = q i ( t ) {\displaystyle q^{i}=q^{i}(t)} q ˙ i = d d t q i ( t ) {\displaystyle {\dot {q}}^{i}={\tfrac {d}{dt}}q^{i}(t)} , obeying Lagrange's equations : d d t ∂ L ∂ q ˙ i − ∂ L ∂ q i = 0 . {\displaystyle {\frac {\mathrm {d} }{\mathrm {d} t}}{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial {\dot {q}}^{i}}}-{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial q^{i}}}=0\ .}
Rearranging and writing in terms of the on-shell p i = p i ( t ) {\displaystyle p_{i}=p_{i}(t)} ∂ L ∂ q i = p ˙ i . {\displaystyle {\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial q^{i}}}={\dot {p}}_{i}\ .}
Thus Lagrange's equations are equivalent to Hamilton's equations: ∂ H ∂ q i = − p ˙ i , ∂ H ∂ p i = q ˙ i , ∂ H ∂ t = − ∂ L ∂ t . {\displaystyle {\frac {\partial {\mathcal {H}}}{\partial q^{i}}}=-{\dot {p}}_{i}\quad ,\quad {\frac {\partial {\mathcal {H}}}{\partial p_{i}}}={\dot {q}}^{i}\quad ,\quad {\frac {\partial {\mathcal {H}}}{\partial t}}=-{\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial t}}\,.}
In the case of time-independent H {\displaystyle {\mathcal {H}}} L {\displaystyle {\mathcal {L}}} , i.e. ∂ H / ∂ t = − ∂ L / ∂ t = 0 {\displaystyle \partial {\mathcal {H}}/\partial t=-\partial {\mathcal {L}}/\partial t=0} , Hamilton's equations consist of 2n first-order differential equations , while Lagrange's equations consist of n second-order equations. Hamilton's equations usually do not reduce the difficulty of finding explicit solutions, but important theoretical results can be derived from them, because coordinates and momenta are independent variables with nearly symmetric roles.
Hamilton's equations have another advantage over Lagrange's equations: if a system has a symmetry, so that some coordinate q i {\displaystyle q_{i}} cyclic coordinate ), the corresponding momentum coordinate p i {\displaystyle p_{i}} n coordinates to (n − 1) coordinates: this is the basis of symplectic reduction in geometry. In the Lagrangian framework, the conservation of momentum also follows immediately, however all the generalized velocities q ˙ i {\displaystyle {\dot {q}}_{i}} n coordinates still has to be solved.[ 4]
The Lagrangian and Hamiltonian approaches provide the groundwork for deeper results in classical mechanics, and suggest analogous formulations in quantum mechanics : the path integral formulation and the Schrödinger equation .
Properties of the Hamiltonian [ edit ] Hamiltonian as the total system energy [ edit ] In its application to a given system, the Hamiltonian is often taken to be H = T + V {\displaystyle {\mathcal {H}}=T+V}
where T {\displaystyle T} V {\displaystyle V}
The relation holds true for nonrelativistic systems when all of the following conditions are satisfied[ 5] [ 6] ∂ V ( q , q ˙ , t ) ∂ q ˙ i = 0 , ∀ i {\displaystyle {\frac {\partial V({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{i}}}=0\;,\quad \forall i} ∂ T ( q , q ˙ , t ) ∂ t = 0 {\displaystyle {\frac {\partial T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)}{\partial t}}=0} T ( q , q ˙ ) = ∑ i = 1 n ∑ j = 1 n ( c i j ( q ) q ˙ i q ˙ j ) {\displaystyle T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\sum _{j=1}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{ij}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{i}{\dot {q}}_{j}{\biggr )}}
where t {\displaystyle t} n {\displaystyle n} c i j ( q ) {\displaystyle c_{ij}({\boldsymbol {q}})} q {\displaystyle {\boldsymbol {q}}}
In words, this means that the relation H = T + V {\displaystyle {\mathcal {H}}=T+V} T {\displaystyle T} scleronomic ), V {\displaystyle V} T {\displaystyle T}
Preliminary to this proof, it is important to address an ambiguity in the related mathematical notation. While a change of variables can be used to equate L ( p , q , t ) = L ( q , q ˙ , t ) {\displaystyle {\mathcal {L}}({\boldsymbol {p}},{\boldsymbol {q}},t)={\mathcal {L}}({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)} ∂ L ( q , q ˙ , t ) ∂ q ˙ i ≠ ∂ L ( p , q , t ) ∂ q ˙ i {\displaystyle {\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{i}}}\neq {\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}({\boldsymbol {p}},{\boldsymbol {q}},t)}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{i}}}} multivariable chain rule should be used. Hence, to avoid ambiguity, the function arguments of any term inside of a partial derivative should be stated.
Additionally, this proof uses the notation f ( a , b , c ) = f ( a , b ) {\displaystyle f(a,b,c)=f(a,b)} ∂ f ( a , b , c ) ∂ c = 0 {\displaystyle {\frac {\partial f(a,b,c)}{\partial c}}=0}
Proof Starting from definitions of the Hamiltonian, generalized momenta, and Lagrangian for an n {\displaystyle n} H = ∑ i = 1 n ( p i q ˙ i ) − L ( q , q ˙ , t ) {\displaystyle {\mathcal {H}}=\sum _{i=1}^{n}{\biggl (}p_{i}{\dot {q}}_{i}{\biggr )}-{\mathcal {L}}({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)} p i ( q , q ˙ , t ) = ∂ L ( q , q ˙ , t ) ∂ q ˙ i {\displaystyle p_{i}({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)={\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{i}}}} L ( q , q ˙ , t ) = T ( q , q ˙ , t ) − V ( q , q ˙ , t ) {\displaystyle {\mathcal {L}}({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)=T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)-V({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)}
Substituting the generalized momenta into the Hamiltonian gives H = ∑ i = 1 n ( ∂ L ( q , q ˙ , t ) ∂ q ˙ i q ˙ i ) − L ( q , q ˙ , t ) {\displaystyle {\mathcal {H}}=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left({\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{i}}}{\dot {q}}_{i}\right)-{\mathcal {L}}({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)}
Substituting the Lagrangian into the result gives H = ∑ i = 1 n ( ∂ ( T ( q , q ˙ , t ) − V ( q , q ˙ , t ) ) ∂ q ˙ i q ˙ i ) − ( T ( q , q ˙ , t ) − V ( q , q ˙ , t ) ) = ∑ i = 1 n ( ∂ T ( q , q ˙ , t ) ∂ q ˙ i q ˙ i − ∂ V ( q , q ˙ , t ) ∂ q ˙ i q ˙ i ) − T ( q , q ˙ , t ) + V ( q , q ˙ , t ) {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\mathcal {H}}&=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left({\frac {\partial \left(T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)-V({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)\right)}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{i}}}{\dot {q}}_{i}\right)-\left(T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)-V({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)\right)\\&=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left({\frac {\partial T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{i}}}{\dot {q}}_{i}-{\frac {\partial V({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{i}}}{\dot {q}}_{i}\right)-T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)+V({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)\end{aligned}}}
Now assume that ∂ V ( q , q ˙ , t ) ∂ q ˙ i = 0 , ∀ i {\displaystyle {\frac {\partial V({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{i}}}=0\;,\quad \forall i}
and also assume that ∂ T ( q , q ˙ , t ) ∂ t = 0 {\displaystyle {\frac {\partial T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)}{\partial t}}=0}
Applying these assumptions results in H = ∑ i = 1 n ( ∂ T ( q , q ˙ ) ∂ q ˙ i q ˙ i − ∂ V ( q , t ) ∂ q ˙ i q ˙ i ) − T ( q , q ˙ ) + V ( q , t ) = ∑ i = 1 n ( ∂ T ( q , q ˙ ) ∂ q ˙ i q ˙ i ) − T ( q , q ˙ ) + V ( q , t ) {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\mathcal {H}}&=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left({\frac {\partial T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{i}}}{\dot {q}}_{i}-{\frac {\partial V({\boldsymbol {q}},t)}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{i}}}{\dot {q}}_{i}\right)-T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})+V({\boldsymbol {q}},t)\\&=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left({\frac {\partial T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{i}}}{\dot {q}}_{i}\right)-T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})+V({\boldsymbol {q}},t)\end{aligned}}}
Next assume that T is of the form T ( q , q ˙ ) = ∑ i = 1 n ∑ j = 1 n ( c i j ( q ) q ˙ i q ˙ j ) {\displaystyle T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\sum _{j=1}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{ij}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{i}{\dot {q}}_{j}{\biggr )}}
where each c i j ( q ) {\displaystyle c_{ij}({\boldsymbol {q}})} q {\displaystyle {\boldsymbol {q}}}
Differentiating this with respect to q ˙ l {\displaystyle {\dot {q}}_{l}} l ∈ [ 1 , n ] {\displaystyle l\in [1,n]} ∂ T ( q , q ˙ ) ∂ q ˙ l = ∑ i = 1 n ∑ j = 1 n ( ∂ [ c i j ( q ) q ˙ i q ˙ j ] ∂ q ˙ l ) = ∑ i = 1 n ∑ j = 1 n ( c i j ( q ) ∂ [ q ˙ i q ˙ j ] ∂ q ˙ l ) {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\frac {\partial T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{l}}}&=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\sum _{j=1}^{n}{\biggl (}{\frac {\partial \left[c_{ij}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{i}{\dot {q}}_{j}\right]}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{l}}}{\biggr )}\\&=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\sum _{j=1}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{ij}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\frac {\partial \left[{\dot {q}}_{i}{\dot {q}}_{j}\right]}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{l}}}{\biggr )}\end{aligned}}}
Splitting the summation, evaluating the partial derivative, and rejoining the summation gives ∂ T ( q , q ˙ ) ∂ q ˙ l = ∑ i ≠ l n ∑ j ≠ l n ( c i j ( q ) ∂ [ q ˙ i q ˙ j ] ∂ q ˙ l ) + ∑ i ≠ l n ( c i l ( q ) ∂ [ q ˙ i q ˙ l ] ∂ q ˙ l ) + ∑ j ≠ l n ( c l j ( q ) ∂ [ q ˙ l q ˙ j ] ∂ q ˙ l ) + c l l ( q ) ∂ [ q ˙ l 2 ] ∂ q ˙ l = ∑ i ≠ l n ∑ j ≠ l n ( 0 ) + ∑ i ≠ l n ( c i l ( q ) q ˙ i ) + ∑ j ≠ l n ( c l j ( q ) q ˙ j ) + 2 c l l ( q ) q ˙ l = ∑ i = 1 n ( c i l ( q ) q ˙ i ) + ∑ j = 1 n ( c l j ( q ) q ˙ j ) {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\frac {\partial T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{l}}}&=\sum _{i\neq l}^{n}\sum _{j\neq l}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{ij}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\frac {\partial \left[{\dot {q}}_{i}{\dot {q}}_{j}\right]}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{l}}}{\biggr )}+\sum _{i\neq l}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{il}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\frac {\partial \left[{\dot {q}}_{i}{\dot {q}}_{l}\right]}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{l}}}{\biggr )}+\sum _{j\neq l}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{lj}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\frac {\partial \left[{\dot {q}}_{l}{\dot {q}}_{j}\right]}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{l}}}{\biggr )}+c_{ll}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\frac {\partial \left[{\dot {q}}_{l}^{2}\right]}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{l}}}\\&=\sum _{i\neq l}^{n}\sum _{j\neq l}^{n}{\biggl (}0{\biggr )}+\sum _{i\neq l}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{il}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{i}{\biggr )}+\sum _{j\neq l}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{lj}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{j}{\biggr )}+2c_{ll}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{l}\\&=\sum _{i=1}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{il}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{i}{\biggr )}+\sum _{j=1}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{lj}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{j}{\biggr )}\end{aligned}}}
Summing (this multiplied by q ˙ l {\displaystyle {\dot {q}}_{l}} l {\displaystyle l} ∑ l = 1 n ( ∂ T ( q , q ˙ ) ∂ q ˙ l q ˙ l ) = ∑ l = 1 n ( ( ∑ i = 1 n ( c i l ( q ) q ˙ i ) + ∑ j = 1 n ( c l j ( q ) q ˙ j ) ) q ˙ l ) = ∑ l = 1 n ∑ i = 1 n ( c i l ( q ) q ˙ i q ˙ l ) + ∑ l = 1 n ∑ j = 1 n ( c l j ( q ) q ˙ j q ˙ l ) = ∑ i = 1 n ∑ l = 1 n ( c i l ( q ) q ˙ i q ˙ l ) + ∑ l = 1 n ∑ j = 1 n ( c l j ( q ) q ˙ l q ˙ j ) = T ( q , q ˙ ) + T ( q , q ˙ ) = 2 T ( q , q ˙ ) {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\sum _{l=1}^{n}\left({\frac {\partial T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{l}}}{\dot {q}}_{l}\right)&=\sum _{l=1}^{n}\left(\left(\sum _{i=1}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{il}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{i}{\biggr )}+\sum _{j=1}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{lj}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{j}{\biggr )}\right){\dot {q}}_{l}\right)\\&=\sum _{l=1}^{n}\sum _{i=1}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{il}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{i}{\dot {q}}_{l}{\biggr )}+\sum _{l=1}^{n}\sum _{j=1}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{lj}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{j}{\dot {q}}_{l}{\biggr )}\\&=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\sum _{l=1}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{il}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{i}{\dot {q}}_{l}{\biggr )}+\sum _{l=1}^{n}\sum _{j=1}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{lj}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{l}{\dot {q}}_{j}{\biggr )}\\&=T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})+T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})\\&=2T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})\end{aligned}}}
This simplification is a result of Euler's homogeneous function theorem .
Hence, the Hamiltonian becomes H = ∑ i = 1 n ( ∂ T ( q , q ˙ ) ∂ q ˙ i q ˙ i ) − T ( q , q ˙ ) + V ( q , t ) = 2 T ( q , q ˙ ) − T ( q , q ˙ ) + V ( q , t ) = T ( q , q ˙ ) + V ( q , t ) {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\mathcal {H}}&=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left({\frac {\partial T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{i}}}{\dot {q}}_{i}\right)-T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})+V({\boldsymbol {q}},t)\\&=2T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})-T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})+V({\boldsymbol {q}},t)\\&=T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})+V({\boldsymbol {q}},t)\end{aligned}}}
Application to systems of point masses [ edit ] For a system of point masses, the requirement for T {\displaystyle T} T ( q , q ˙ , t ) = T ( q , q ˙ ) {\displaystyle T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)=T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})} H = T + V {\displaystyle {\mathcal {H}}=T+V}
Proof Consider the kinetic energy for a system of N point masses. If it is assumed that T ( q , q ˙ , t ) = T ( q , q ˙ ) {\displaystyle T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)=T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})} r ˙ k ( q , q ˙ , t ) = r ˙ k ( q , q ˙ ) {\displaystyle {\dot {\mathbf {r} }}_{k}({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)={\dot {\mathbf {r} }}_{k}({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})} Scleronomous § Application T ( q , q ˙ ) = 1 2 ∑ k = 1 N ( m k r ˙ k ( q , q ˙ ) ⋅ r ˙ k ( q , q ˙ ) ) {\displaystyle T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})={\frac {1}{2}}\sum _{k=1}^{N}{\biggl (}m_{k}{\dot {\mathbf {r} }}_{k}({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})\cdot {\dot {\mathbf {r} }}_{k}({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}}){\biggr )}}
The chain rule for many variables can be used to expand the velocity r ˙ k ( q , q ˙ ) = d r k ( q ) d t = ∑ i = 1 n ( ∂ r k ( q ) ∂ q i q ˙ i ) {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\dot {\mathbf {r} }}_{k}({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})&={\frac {d\mathbf {r} _{k}({\boldsymbol {q}})}{dt}}\\&=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left({\frac {\partial \mathbf {r} _{k}({\boldsymbol {q}})}{\partial q_{i}}}{\dot {q}}_{i}\right)\end{aligned}}}
Resulting in T ( q , q ˙ ) = 1 2 ∑ k = 1 N ( m k ( ∑ i = 1 n ( ∂ r k ( q ) ∂ q i q ˙ i ) ⋅ ∑ j = 1 n ( ∂ r k ( q ) ∂ q j q ˙ j ) ) ) = ∑ k = 1 N ∑ i = 1 n ∑ j = 1 n ( 1 2 m k ∂ r k ( q ) ∂ q i ⋅ ∂ r k ( q ) ∂ q j q ˙ i q ˙ j ) = ∑ i = 1 n ∑ j = 1 n ( ∑ k = 1 N ( 1 2 m k ∂ r k ( q ) ∂ q i ⋅ ∂ r k ( q ) ∂ q j ) q ˙ i q ˙ j ) = ∑ i = 1 n ∑ j = 1 n ( c i j ( q ) q ˙ i q ˙ j ) {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})&={\frac {1}{2}}\sum _{k=1}^{N}\left(m_{k}\left(\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left({\frac {\partial \mathbf {r} _{k}({\boldsymbol {q}})}{\partial q_{i}}}{\dot {q}}_{i}\right)\cdot \sum _{j=1}^{n}\left({\frac {\partial \mathbf {r} _{k}({\boldsymbol {q}})}{\partial q_{j}}}{\dot {q}}_{j}\right)\right)\right)\\&=\sum _{k=1}^{N}\sum _{i=1}^{n}\sum _{j=1}^{n}\left({\frac {1}{2}}m_{k}{\frac {\partial \mathbf {r} _{k}({\boldsymbol {q}})}{\partial q_{i}}}\cdot {\frac {\partial \mathbf {r} _{k}({\boldsymbol {q}})}{\partial q_{j}}}{\dot {q}}_{i}{\dot {q}}_{j}\right)\\&=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\sum _{j=1}^{n}\left(\sum _{k=1}^{N}\left({\frac {1}{2}}m_{k}{\frac {\partial \mathbf {r} _{k}({\boldsymbol {q}})}{\partial q_{i}}}\cdot {\frac {\partial \mathbf {r} _{k}({\boldsymbol {q}})}{\partial q_{j}}}\right){\dot {q}}_{i}{\dot {q}}_{j}\right)\\&=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\sum _{j=1}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{ij}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{i}{\dot {q}}_{j}{\biggr )}\end{aligned}}}
This is of the required form.
Conservation of energy [ edit ] If the conditions for H = T + V {\displaystyle {\mathcal {H}}=T+V} V {\displaystyle V}
∂ V ( q , q ˙ , t ) ∂ t = 0 {\displaystyle {\frac {\partial V({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}},t)}{\partial t}}=0}
With respect to the extended Euler-Lagrange formulation (See Lagrangian mechanics § Extensions to include non-conservative forces Rayleigh dissipation function represents energy dissipation by nature. Therefore, energy is not conserved when R ≠ 0 {\displaystyle R\neq 0}
In summary, the requirements for H = T + V = constant of time {\displaystyle {\mathcal {H}}=T+V={\text{constant of time}}} [ 5] [ 6]
V = V ( q ) {\displaystyle V=V({\boldsymbol {q}})} T = T ( q , q ˙ ) {\displaystyle T=T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})} T {\displaystyle T} q ˙ {\displaystyle {\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}}} Hamiltonian of a charged particle in an electromagnetic field [ edit ] A sufficient illustration of Hamiltonian mechanics is given by the Hamiltonian of a charged particle in an electromagnetic field . In Cartesian coordinates the Lagrangian of a non-relativistic classical particle in an electromagnetic field is (in SI Units ): L = ∑ i 1 2 m x ˙ i 2 + ∑ i q x ˙ i A i − q φ , {\displaystyle {\mathcal {L}}=\sum _{i}{\tfrac {1}{2}}m{\dot {x}}_{i}^{2}+\sum _{i}q{\dot {x}}_{i}A_{i}-q\varphi ,} q is the electric charge of the particle, φ is the electric scalar potential , and the Ai are the components of the magnetic vector potential that may all explicitly depend on x i {\displaystyle x_{i}} t {\displaystyle t} .
This Lagrangian, combined with Euler–Lagrange equation , produces the Lorentz force law m x ¨ = q E + q x ˙ × B , {\displaystyle m{\ddot {\mathbf {x} }}=q\mathbf {E} +q{\dot {\mathbf {x} }}\times \mathbf {B} \,,} minimal coupling .
The canonical momenta are given by: p i = ∂ L ∂ x ˙ i = m x ˙ i + q A i . {\displaystyle p_{i}={\frac {\partial {\mathcal {L}}}{\partial {\dot {x}}_{i}}}=m{\dot {x}}_{i}+qA_{i}.}
The Hamiltonian, as the Legendre transformation of the Lagrangian, is therefore: H = ∑ i x ˙ i p i − L = ∑ i ( p i − q A i ) 2 2 m + q φ . {\displaystyle {\mathcal {H}}=\sum _{i}{\dot {x}}_{i}p_{i}-{\mathcal {L}}=\sum _{i}{\frac {\left(p_{i}-qA_{i}\right)^{2}}{2m}}+q\varphi .}
This equation is used frequently in quantum mechanics .
Under gauge transformation : A → A + ∇ f , φ → φ − f ˙ , {\displaystyle \mathbf {A} \rightarrow \mathbf {A} +\nabla f\,,\quad \varphi \rightarrow \varphi -{\dot {f}}\,,} f (r , t ) L → L ′ = L + q d f d t , p → p ′ = p + q ∇ f , H → H ′ = H − q ∂ f ∂ t , {\displaystyle L\rightarrow L'=L+q{\frac {df}{dt}}\,,\quad \mathbf {p} \rightarrow \mathbf {p'} =\mathbf {p} +q\nabla f\,,\quad H\rightarrow H'=H-q{\frac {\partial f}{\partial t}}\,,} ∂ H ′ ∂ x i | p i ′ = ∂ ∂ x i | p i ′ ( x ˙ i p i ′ − L ′ ) = − ∂ L ′ ∂ x i | p i ′ = − ∂ L ∂ x i | p i ′ − q ∂ ∂ x i | p i ′ d f d t = − d d t ( ∂ L ∂ x ˙ i | p i ′ + q ∂ f ∂ x i | p i ′ ) = − p ˙ i ′ {\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\left.{\frac {\partial H'}{\partial {x_{i}}}}\right|_{p'_{i}}&=\left.{\frac {\partial }{\partial {x_{i}}}}\right|_{p'_{i}}({\dot {x}}_{i}p'_{i}-L')=-\left.{\frac {\partial L'}{\partial {x_{i}}}}\right|_{p'_{i}}\\&=-\left.{\frac {\partial L}{\partial {x_{i}}}}\right|_{p'_{i}}-q\left.{\frac {\partial }{\partial {x_{i}}}}\right|_{p'_{i}}{\frac {df}{dt}}\\&=-{\frac {d}{dt}}\left(\left.{\frac {\partial L}{\partial {{\dot {x}}_{i}}}}\right|_{p'_{i}}+q\left.{\frac {\partial f}{\partial {x_{i}}}}\right|_{p'_{i}}\right)\\&=-{\dot {p}}'_{i}\end{aligned}}}
In quantum mechanics, the wave function will also undergo a local U(1) group transformation[ 7]
Relativistic charged particle in an electromagnetic field [ edit ] The relativistic Lagrangian for a particle (rest mass m {\displaystyle m} charge q {\displaystyle q} ) is given by:
L ( t ) = − m c 2 1 − x ˙ ( t ) 2 c 2 + q x ˙ ( t ) ⋅ A ( x ( t ) , t ) − q φ ( x ( t ) , t ) {\displaystyle {\mathcal {L}}(t)=-mc^{2}{\sqrt {1-{\frac {{{\dot {\mathbf {x} }}(t)}^{2}}{c^{2}}}}}+q{\dot {\mathbf {x} }}(t)\cdot \mathbf {A} \left(\mathbf {x} (t),t\right)-q\varphi \left(\mathbf {x} (t),t\right)}
Thus the particle's canonical momentum is p ( t ) = ∂ L ∂ x ˙ = m
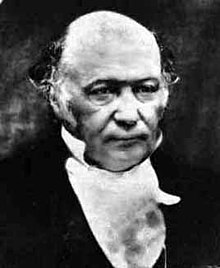



 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch































![{\displaystyle {\boldsymbol {q}}:[a,b]\to M}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/990de891d10ad37bb4492f70cce6580acffc2abb)



![{\displaystyle {\mathcal {S}}[{\boldsymbol {q}}]=\int _{a}^{b}{\mathcal {L}}(t,{\boldsymbol {q}}(t),{\dot {\boldsymbol {q}}}(t))\,dt=\int _{a}^{b}\left(\sum _{i=1}^{n}p_{i}{\dot {q}}^{i}-{\mathcal {H}}({\boldsymbol {p}},{\boldsymbol {q}},t)\right)\,dt,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8019c0d9b1978276493ae6a9635878b6cf13659c)











![{\displaystyle H=\underbrace {\left[{\frac {1}{2}}m\ell ^{2}{\dot {\theta }}^{2}+{\frac {1}{2}}m\ell ^{2}\sin ^{2}\!\theta \,{\dot {\varphi }}^{2}\right]} _{T}+\underbrace {{\Big [}-mg\ell \cos \theta {\Big ]}} _{V}={\frac {P_{\theta }^{2}}{2m\ell ^{2}}}+{\frac {P_{\varphi }^{2}}{2m\ell ^{2}\sin ^{2}\theta }}-mg\ell \cos \theta .}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/acbd62626a60945bf1c5c52d8ae3df7f0abc55c5)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\dot {\theta }}&={P_{\theta } \over m\ell ^{2}}\\[6pt]{\dot {\varphi }}&={P_{\varphi } \over m\ell ^{2}\sin ^{2}\theta }\\[6pt]{\dot {P_{\theta }}}&={P_{\varphi }^{2} \over m\ell ^{2}\sin ^{3}\theta }\cos \theta -mg\ell \sin \theta \\[6pt]{\dot {P_{\varphi }}}&=0.\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/134880330383c7f07ee281125b3e9c1934c67674)



























































![{\displaystyle l\in [1,n]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0ccea7c07db9b24d259507bc00a07f694f264b00)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\frac {\partial T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{l}}}&=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\sum _{j=1}^{n}{\biggl (}{\frac {\partial \left[c_{ij}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{i}{\dot {q}}_{j}\right]}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{l}}}{\biggr )}\\&=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\sum _{j=1}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{ij}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\frac {\partial \left[{\dot {q}}_{i}{\dot {q}}_{j}\right]}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{l}}}{\biggr )}\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/be042b0b8af71cff1a0832d7c8038ee367819c61)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\frac {\partial T({\boldsymbol {q}},{\boldsymbol {\dot {q}}})}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{l}}}&=\sum _{i\neq l}^{n}\sum _{j\neq l}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{ij}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\frac {\partial \left[{\dot {q}}_{i}{\dot {q}}_{j}\right]}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{l}}}{\biggr )}+\sum _{i\neq l}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{il}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\frac {\partial \left[{\dot {q}}_{i}{\dot {q}}_{l}\right]}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{l}}}{\biggr )}+\sum _{j\neq l}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{lj}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\frac {\partial \left[{\dot {q}}_{l}{\dot {q}}_{j}\right]}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{l}}}{\biggr )}+c_{ll}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\frac {\partial \left[{\dot {q}}_{l}^{2}\right]}{\partial {\dot {q}}_{l}}}\\&=\sum _{i\neq l}^{n}\sum _{j\neq l}^{n}{\biggl (}0{\biggr )}+\sum _{i\neq l}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{il}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{i}{\biggr )}+\sum _{j\neq l}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{lj}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{j}{\biggr )}+2c_{ll}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{l}\\&=\sum _{i=1}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{il}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{i}{\biggr )}+\sum _{j=1}^{n}{\biggl (}c_{lj}({\boldsymbol {q}}){\dot {q}}_{j}{\biggr )}\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/862080e8c2548a484e93e9487a5ac60d82918b73)























