Acide 3-hydroxybenzoïque — Wikipédia
| Acide 3-hydroxybenzoïque | |
 | |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | acide 3-hydroxybenzoïque |
| Synonymes | acide métahydroxybenzoïque |
| No CAS | |
| No ECHA | 100.002.478 |
| No CE | 202-726-5 |
| No RTECS | DH1924980 |
| PubChem | 7420 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Apparence | cristal incolore |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C7H6O3 [Isomères] |
| Masse molaire[2] | 138,120 7 ± 0,006 9 g/mol C 60,87 %, H 4,38 %, O 34,75 %, |
| pKa | 4,3 à 258 °C[1] |
| Propriétés physiques | |
| T° fusion | 200 °C[3] |
| Solubilité | 7,250 g·l-1 (eau, 25 °C)[1] |
| Précautions | |
| SGH | |
| H302, H315, H319, H335, P261 et P305+P351+P338 | |
| Directive 67/548/EEC[4] | |
| Écotoxicologie | |
| DL50 | 2 g·kg-1 (souris, oral)[5] |
| LogP | 1,5[1] |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
| modifier | |
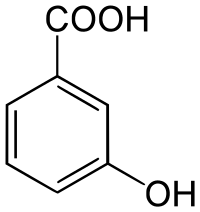
L'acide 3-hydroxybenzoïque ou acide métahydroxybenzoïque est un composé organique aromatique. C'est l'un des trois isomère de l'acide hydroxybenzoïque, avec l'acide salicylique (acide 2-hydroxybenzoïque) et l'acide parahydroxybenzoïque (acide 4-hydroxybenzoïque).
Il peut être naturellement formé à partir de l'acide 3-chlorobenzoïque par certaines bactéries du genre Pseudomonas[6].
Notes et références
[modifier | modifier le code]- (en) « Acide 3-hydroxybenzoïque », sur ChemIDplus, consulté le 7 juillet 2011
- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- CRC Handbook of Tables for Organic Compound Identification, Third Edition, 1984, (ISBN 0-8493-0303-6).
- Fiche Sigma-Aldrich du composé acide 3-hydroxybenzoïque, consultée le 5 juillet 2011.
- Quarterly Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmacology. Vol. 19, Pg. 483, 1946.
- H.W. Johnston, G.G. Briggs and M. Alexander, « Metabolism of 3-chlorobenzoic acid by a pseudomonad », Soil Biology and Biochemistry, vol. 4, no 2, , p. 187–190 (DOI 10.1016/0038-0717(72)90010-7)


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch
