Hexanol — Wikipédia
Le terme hexanol en chimie organique peut faire référence aux 28 isomères - en comptant les énantiomères- de formule brute C6H14O :
Structure Type Nomenclature IUPAC Numéro CAS Température d'ébullition (°C) 
Primaire hexan-1-ol 158,2 
Secondaire (RS)-hexan-2-ol , (RS)
(R)
(S)139,7 Secondaire (RS)-hexan-3-ol (RS)
(R)
(S)135 Primaire (RS)-2-méthylpentan-1-ol (RS)
(R)
(S)148 Primaire (RS)-3-méthylpentan-1-ol , (RS)
(R)(–)
, (S)(+)153 Primaire 4-méthylpentan-1-ol 151,6 Tertiaire 2-méthylpentan-2-ol 121,4 Secondaire (RRSS)-3-méthylpentan-2-ol
, (RR)
(SS)
(2R3S)
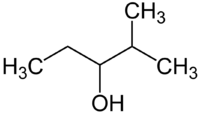
(2S3R)133,5 Secondaire (RS)-4-méthylpentan-2-ol (RS)
(R)
(S)133,5 Secondaire (RS)-2-méthylpentan-3-ol (RS)
(R)
(S)126,5 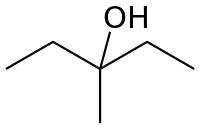
Tertiaire 3-méthylpentan-3-ol 122,4 
Primaire 2,2-diméthylbutan-1-ol 136,5 Primaire (RS)-2,3-diméthylbutan-1-ol , (RS)
(R)
(S)142 Primaire 3,3-diméthylbutan-1-ol 143 Tertiaire 2,3-diméthylbutan-2-ol 117,8 Secondaire (RS)-3,3-diméthylbutan-2-ol (RS)
(R)
(S)117,8 Primaire 2-éthylbutan-1-ol 146,5


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch