1,2,3,4,6-Pentagalloyl glucose — Wikipédia
| 1,2,3,4,6-Pentagalloyl glucose | |
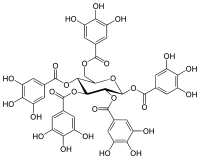 | |
| Formule développée. | |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| No CAS | |
| No ECHA | 100.113.489 |
| SMILES | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C41H32O26 |
| Masse molaire[1] | 940,677 2 ± 0,042 8 g/mol C 52,35 %, H 3,43 %, O 44,22 %, |
| Propriétés physiques | |
| T° fusion | Point de sublimation : |
| Solubilité | méthanol / acétone |
| Propriétés optiques | |
| Spectre d’absorption | 279,7 nm (lambda max) |
| Composés apparentés | |
| Autres composés | |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
| modifier | |
Le 1,2,3,4,6-Pentagalloyl glucose (PGG en abrégé) est un gallotanin, un type de tanins hydrolysables.
Références
[modifier | modifier le code]- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) Hagerman A.E., Rice M.E. & Ritchard N.T., 1998. Mechanisms of Protein Precipitation for Two Tannins, Pentagalloyl Glucose and Epicatechin (4→8) Catechin (Procyanidin). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 46 (7): 2590–2595, DOI 10.1021/jf971097k.
Liens externes
[modifier | modifier le code]- Ressource relative à la santé :


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch