Osteoporosis - Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
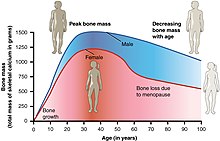
Osteoporosis is the weakening of bones in the body. It is caused by lack of calcium in the bones. This causes the bones to become brittle. They break easily. Side effects include limping. Some symptoms late in the disease include pain in the bones, bones breaking very easily and lower back pain due to spinal bone fractures.[1] It is more likely for a woman to get osteoporosis than a man.[2] Elderly people are more likely to develop osteoporosis than younger people. The amount of calcium in the bones decreases as a person gets older. There are three kinds of osteoporosis.
There is no cure for osteoporosis. A person can keep it from happening by exercising and taking the right amount of calcium each day. 75 million people in the United States, Japan, and Europe have osteoporosis. 30 million people in the US have poor bone density. Vitamin D, calcium, and exercise are the three main things for healthy bones. Consuming too much alcohol and caffeine can cause an increase in the risk of weak bones. Too much salt increases the amount of calcium lost in urine. This is bad because calcium makes bones strong. People should not take iron and calcium supplements at the same time. This is because calcium competes with the absorption of minerals such as iron.[3]
References
[change | change source]- ↑ "Google Health - Osteoporosis". Google/A.D.A.M. Retrieved 2009-11-16.
- ↑ "Osteoporosis Risk factors". Mayo Clinic.
- ↑ Gale Encyclopedia of Diets, 2nd ed., Detroit: Gale, 2013, pp. 882-889.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch