Triangle - Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia

A triangle is a shape, or a part of two dimensional space. It has three straight sides and three vertices. The three angles of a triangle always add up to 180° (180 degrees). It is the polygon with the least possible number of sides. A triangle with vertices A, B, C is written as .[1][2] The study of geometry related to triangles is called trigonometry. Modern computers usually use triangles to make more complex graphic images or shapes.
Types of triangles
[change | change source]
Triangles can be grouped according to how many of their sides are equal:[3]
- if all the three sides of a triangle have the same length, then it is an equilateral triangle.
- if a triangle has two sides with the same length, then it is an isosceles triangle.
- if all the three sides of a triangle have different lengths, then we have a scalene triangle.
Triangles can also be grouped by their angles:[3]
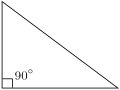
- if a triangle has a right angle, that is, if one of the angles of that triangle measures 90° (90 degrees), then it is a right triangle. The opposite side to the right angle is the hypotenuse.
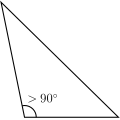
- if a triangle has an obtuse angle, that is, if one of the angles of that triangle is larger than 90°, then it is an obtuse triangle.
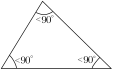
- if a triangle has only acute angles, that is, if all the angles of that triangle are less than 90°, then it is an acute triangle.
|
Area
[change | change source]The area of a triangle is equal to base times height times one half.
Related pages
[change | change source]References
[change | change source]- ↑ "List of Geometry and Trigonometry Symbols". Math Vault. 2020-04-17. Retrieved 2020-09-01.
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W. "Triangle". mathworld.wolfram.com. Retrieved 2020-09-01.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Triangles - Equilateral, Isosceles and Scalene". www.mathsisfun.com. Retrieved 2020-09-01.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch