2015 in archosaur paleontology
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
This article records new taxa of fossil archosaurs of every kind that are scheduled described during the year 2015, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleontology of archosaurs that are scheduled to occur in the year 2015.
Pseudosuchians
[edit]Research
[edit]- Revision of the type material of Rauisuchus tiradentes is published by Lautenschlager and Rauhut (2015).[1]
- A study on the changes in the morphology of vertebrae caused by increased adaptation to aquatic locomotion in the evolution of crocodylomorphs is published by Molnar et al. (2015).[2]
- A study of the evolutionary history of the clade Crocodyliformes is published by Bronzati, Montefeltro and Langer (2015).[3]
- A study of impact of the climate changes on the evolution and biodiversity of pseudosuchian archosaurs is published by Mannion et al. (2015).[4]
- A study on the phylogenetic position of thalattosuchians within Crocodylomorpha is published by Wilberg (2015).[5]
- A review of the diagnostic features of the species assigned to the genus Machimosaurus is published by Martin, Vincent & Falconnet (2015).[6]
- An isolated metriorhynchid tooth is described from the Early Cretaceous (Aptian) Hybla Formation (Sicily, Italy) by Chiarenza et al. (2015), extending the known geological range of Metriorhynchidae and Thalattosuchia by approximately 7–8 million years;[7] Fischer et al. (2015) subsequently caution that it might potentially be a pliosaurid tooth instead.[8]
New taxa
[edit]| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Unit | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Wu & Brinkman | Latest Cretaceous | A crocodylian, probably a crocodyloid. The type species is Albertosuchus knudsenii. | ||||
| Sp. nov | Valid | Blanco et al. | Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) | A eusuchian crocodylomorph, a species of Allodaposuchus. | ||||
| Sp. nov | Valid | Salas-Gismondi et al. | Late Middle Miocene | |||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Zanno et al. | Late Triassic (Carnian) | An early member of Crocodylomorpha. The type species is Carnufex carolinensis. |  | |||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Lacerda, Schultz & Bertoni-Machado | Triassic (late Ladinian/early Carnian) | A non-crocodylomorph loricatan. The type species is Dagasuchus santacruzensis. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Salas-Gismondi et al. | Late Middle Miocene | A caiman. The type species is Gnatusuchus pebasensis. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Heckert et al. | Late Triassic | An aetosaur. The type species is Gorgetosuchus pekinensis. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Sweetman, Pedreira-Segade & Vidovic | Early Cretaceous (Barremian) | A crocodyliform related to Bernissartia. The type species is Koumpiodontosuchus aprosdokiti. |  | |||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Salas-Gismondi et al. | Late Middle Miocene | A caiman. The type species is Kuttanacaiman iquitosensis. | ||||
| Gen. et 2 sp. nov | Valid | Narváez et al. | Late Cretaceous (late Campanian-early Maastrichtian) | A eusuchian crocodyliform related to Allodaposuchus. The type species is Lohuecosuchus megadontos; genus also contains Lohuecosuchus mechinorum. |  | |||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Wilberg | Middle Jurassic (Aalenian–Bajocian) | A thalattosuchian crocodylomorph. The type species is Zoneait nargorum. |
Non-avian dinosaurs
[edit]Research
[edit]- A study of phylogenetic relationships of sauropod dinosaurs belonging to the family Diplodocidae and the taxonomic revision of the family is published by Tschopp, Mateus and Benson (2015); the authors propose to reestablish Brontosaurus as a genus distinct from Apatosaurus and to transfer Dinheirosaurus lourinhanensis to the genus Supersaurus.[18][19]
- Additional information on the anatomy of the holotype specimen of the rebbachisaurid sauropod Tataouinea hannibalis, including description of newly discovered fossil material of this specimen, and study of its phylogenetic relationships is published by Fanti et al. (2015).[20]
- A reevaluation of the estimated body mass of Dreadnoughtus schrani is published by Bates et al. (2015).[21]
- A study of phylogenetic relationships of ornithischian dinosaurs traditionally referred to as ‘basal ornithopods’ or ‘hypsilophodontids’ is published by Boyd (2015).[22]
- Carpenter & Lamanna (2015) reinterpret the ornithopod braincase from the Morrison Formation of the Carnegie Quarry at Dinosaur National Monument (Utah), formerly assigned to Uteodon aphanoecetes, as actually belonging to Dryosaurus cf. D. altus. The authors consider genera Uteodon and Cumnoria to be junior synonyms of Camptosaurus, and transfer the species Cumnoria prestwichii and Uteodon aphanoecetes to the genus Camptosaurus.[23]
New taxa
[edit]| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Unit | Location | Notes | Images | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gen. et comb. nov | Valid | Prieto-Márquez et al. | Late Cretaceous (late Maastrichtian) | A hadrosaurid; a new genus for "Saurolophus" morrisi Prieto-Márquez & Wagner (2013). |  | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Bell & Currie | Late Cretaceous (late Campanian) | A dromaeosaurid theropod. The type species is Boreonykus certekorum. |  | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Novas et al. | Late Jurassic (Tithonian) | A dinosaur of uncertain phylogenetic placement. Originally classified as a theropod dinosaur (a basal member of Tetanurae), but subsequently argued to be an ornithischian.[27] The type species is Chilesaurus diegosuarezi. |  | ||||
| Gen. et comb. nov | Valid[29] | Arbour & Currie | Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian–Turonian) | An ankylosaurine ankylosaurid; a new genus for "Crichtonsaurus" benxiensis Lü, Ji, Gao & Li (2007). | |||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | DePalma et al. | Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) | A member of Dromaeosauridae. The type species is Dakotaraptor steini. |  | ||||
| Eucnemesaurus entaxonis[31] | Sp. nov | Valid | McPhee et al. | Late Triassic | Lower Elliot Formation | A non-sauropod sauropodomorph, a species of Eucnemesaurus. | |||
| Gen. et comb. nov | Valid | Tschopp, Mateus & Benson | Late Jurassic (Kimmeridgian) | A diplodocid sauropod; a new genus for "Diplodocus" hayi Holland (1924). |  | ||||
| Gspsaurus[32] | Gen. et comb. nov | Dubious | Malkani | Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) | Pab Formation | A titanosauriform sauropod. The type species is G. Pakistani. | |||
| Gen. et comb. nov. | Valid | Upchurch, Mannion & Taylor | Early Cretaceous (late Berriasian—Valanginian) | A macronarian sauropod of uncertain phylogenetic placement; a new genus for "Pelorosaurus" becklesii Mantell (1852). |  | ||||
| Gen. et comb. nov | Valid | Blows | Early Cretaceous | A new genus for "Polacanthus" rudgwickensis Blows (1996). | |||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Han et al. | Late Jurassic (Oxfordian) | A basal ceratopsian, possibly a member of Chaoyangsauridae. The type species is Hualianceratops wucaiwanensis. |  | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Lü et al. | Late Cretaceous (Campanian-Maastrichtian) | An oviraptorid theropod. The type species is Huanansaurus ganzhouensis. |  | ||||
| Sp. nov | Valid | Verdú et al. | Early Cretaceous (early Barremian) | An ornithopod, a species of Iguanodon. | |||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | He et al. | Late Cretaceous | A leptoceratopsid ceratopsian. The type species is Ischioceratops zhuchengensis. |  | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Shibata & Azuma | Early Cretaceous | A non-hadrosaurid hadrosauroid. The type species is Koshisaurus katsuyama. |  | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Leahey et al. | Cretaceous (late Albian–(?)early Cenomanian) | Allaru Mudstone | An ankylosaur. The type species is Kunbarrasaurus ieversi. |  | |||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Disputed | Alifanov & Saveliev | Late Jurassic (Tithonian?) | A dinosaur of uncertain phylogenetic placement; considered to be a theropod dinosaur related to Nqwebasaurus by the authors of its description,[41] but subsequently argued to be an ornithischian, possibly synonymous with Kulindadromeus.[42][43] The type species is Lepidocheirosaurus natatilis. | |||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Nesbitt & Ezcurra | Late Triassic | A coelophysoid theropod. The type species is Lepidus praecisio. |  | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Gasulla et al. | Early Cretaceous (probably late Barremian) | An ornithopod dinosaur, a basal member of Styracosterna. The type species is Morelladon beltrani. | |||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Zheng, Jin & Xu | Late Cretaceous (early-middle Turonian—middle Campanian) | A basal neoceratopsian. The type species is Mosaiceratops azumai. |  | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Xing et al. | Middle Jurassic (Aalenian or Bajocian) | A eusauropod sauropod. The type species is Nebulasaurus taito. | |||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Carballido et al. | Early Cretaceous (Barremian) | A brachiosaurid sauropod. The type species is Padillasaurus leivaensis. |  | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Freedman Fowler & Horner | Late Cretaceous (Campanian) | A hadrosaurid. The type species is Probrachylophosaurus bergei. | 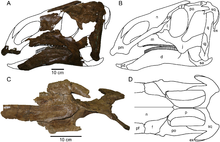 | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | McPhee et al. | Early Jurassic (probably late Hettangian to Sinemurian) | Upper Elliot Formation | A basal sauropod. The type species is Pulanesaura eocollum. |  | |||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Xing et al. | Late Jurassic | A mamenchisaurid sauropod. The type species is Qijianglong guokr. | |||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Brown & Henderson | Late Cretaceous (probably middle Maastrichtian) | A chasmosaurine ceratopsid. The type species is Regaliceratops peterhewsi. |  | ||||
| Sp. nov | Valid | Jasinski | Late Cretaceous (late Campanian) | A member of Dromaeosauridae, a species of Saurornitholestes. | |||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Otero et al. | Late Triassic or Early Jurassic | A non-sauropod sauropodomorph. The type species is Sefapanosaurus zastronensis. | |||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Shibata et al. | Early Cretaceous (Aptian) | A basal member of Hadrosauroidea. The type species is Sirindhorna khoratensis. |  | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Disputed | Mori, Druckenmiller & Erickson | Late Cretaceous (early Maastrichtian) | A saurolophine hadrosaurid. The type species is Ugrunaaluk kuukpikensis. The genus Ugrunaaluk was considered to be a junior synonym of the genus Edmontosaurus by Takasaki et al. (2020).[57] | |||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Evans & Ryan | Late Cretaceous (Campanian) | A centrosaurine ceratopsid. The type species is Wendiceratops pinhornensis. |  | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Xu et al. | Jurassic (Callovian or Oxfordian) | A scansoriopterygid theropod. The type species is Yi qi. |  | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Lü & Brusatte | Early Cretaceous | A dromaeosaurid theropod. The type species is Zhenyuanlong suni. |  |
Birds
[edit]Research
[edit]- Balaur bondoc, originally interpreted as a member of Dromaeosauridae, is argued to be a basal member of Avialae by Cau, Brougham and Naish (2015).[61]
- Estimates of likely mass and flight capability of the extinct Chatham duck (Anas chathamica), as indicated by measurements of major bones, are published by Williams (2015).[62]
- New cranial material of the Oligo-Miocene relative of flamingos, Harrisonavis croizeti, is described by Torres et al. (2015).[63]
- New specimens of the Eocene relative of swifts, Scaniacypselus szarskii, are described by Mayr (2015).[64]
- A specimen of a stem-coliiform Masillacolius brevidactylus with preserved skull is described by Mayr (2015).[65]
- A study of the phylogenetic relationships of Psittacopes, Pumiliornis and Morsoravis, indicating their close relationship to the passerines and extinct family Zygodactylidae, is published by Mayr (2015); the author also introduced a new name, Parapasseres, for the clade containing Passeriformes and Zygodactylidae but not Psittacopes.[66]
- A study of preserved specimens of the Puerto Rican conure (previously considered to be an extinct subspecies of the Hispaniolan parakeet) is published by Olson (2015), who raises it to the rank of a separate species Psittacara maugei.[67]
- A Dwarf Emu was found in the Miocene of Alcoota in Central Australia.[68]
- Jones et al. (2015) describe a distal end of the left tibiotarsus of a member of the genus Caracara of uncertain specific assignment from the late Pleistocene of Argentina, estimated to be the largest member of the family Falconidae described thus far.[69]
- A description of the skeletal anatomy of two well-preserved specimens of the dodo is published by Claessens, Meijer and Hume (2015).[70]
New taxa
[edit]| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Unit | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sp. nov. | Valid | An Old World vulture, Accipitridae, related to the cinereous vulture. | ||||||
| Sp. nov | Valid | Forshaw | Holocene | A new scientific name for the Norfolk ground dove. The previous name used to refer to this species, Columba norfolciensis Latham (1801), was suppressed by ICZN in 2010.[73] | ||||
| Sp. nov. | Valid | Zelenkov & Panteleyev | Late Miocene | An Anatidae. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Wang et al. | A Hongshanornithidae. Type species A. meemannae. |  | ||||
| Sp. nov. | Valid | Early Pliocene | ||||||
| Sp. nov. | Valid | Boev | Early Pleistocene | |||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Carvalho et al. | Aptian | Crato Member, Santana Formation | A member of Euenantiornithes of uncertain phylogenetic placement.[78][79] |  | ||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Wang et al. | Early Cretaceous | A member of Enantiornithes. The type species is D. cuii. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Mayr | Eocene | A bird of uncertain phylogenetic placement. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | O’Connor et al. | Early Cretaceous (Aptian) | A member of Enantiornithes. The type species is Feitianius paradisi. |  | |||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Zhao et al. | Early Eocene | A bird of uncertain phylogenetic placement, possibly a relative of trogons. Type species F. songi. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Bell & Chiappe | Late Cretaceous (late Coniacian—early Campanian) | The Smoky Hill Member of the Niobrara Chalk | A member of Hesperornithiformes. The type species is Fumicollis hoffmani. |  | ||
| Sp. nov. | Valid | Zelenkov & Panteleyev | Middle Turolian | A snipe, Scolopacidae. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid[86] | De Pietri et al. | Early Miocene (19–16 Ma) | A member of Scolopaci of uncertain phylogenetic placement. The type species is Hakawai melvillei. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid[88] | Zelenkov & Averianov | Early Cretaceous | A member of Enantiornithes, probably a relative of Gobipteryx. Type species H. ponomarenkoi. | ||||
| Gen. et comb. nov. | Valid[90] | Early Cretaceous | A member of Enantiornithes of uncertain phylogenetic placement; a new genus for "Cathayornis" caudatus Hou (1997). | |||||
| Sp. nov. | Valid[92] | Holocene | ||||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Wang, Wang & Hu | Early Cretaceous | A basal member of Ornithuromorpha. Type species J. zhangi. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Stucchi et al. | Late Miocene | A condor. Type species K. cardenasi. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid[96] | Stidham & Hilton | Miocene (16.1–14.6 Ma) | A member of Anatidae; a member or a relative of members of the subfamily Oxyurinae. The type species is Lavadytis pyrenae. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Degrange et al. | Late Pliocene | A mesembriornithine phorusrhacid. Type species L. scagliai. |  | |||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Latest Eocene or early Oligocene | A member of Procellariiformes. Type species M. mirae. | |||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Zvonok, Zelenkov & Danilov | Eocene (Bartonian) | Possibly a member of Suliformes. The type species is Mangystania humilicristata. | ||||
| Sp. nov | Valid | Zelenkov | Miocene | A grebe | ||||
| Gen. et comb. nov | Valid | Zelenkov in Zelenkov & Kurochkin | Late Miocene | A member of Rallidae. A new genus for "Tertiariaporphyrula" lungi Kurochkin & Ganea (1972). | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Worthy et al. | Holocene | A megapode. The type species is M. walterlinii. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Middle Eocene | A Psittaciformes incertae sedis. Type species N. praeruptorum. | |||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Elżanowski & Zelenkov | Middle Miocene | An Ardeidae. Type species N. robusta. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Late Oligocene | A member of Charadriiformes related to the plains-wanderer. Type species O. milleri. | |||||
| Sp. nov. | Valid | Agnolin & Chafrat | Early Miocene | |||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Hu, O’Connor & Zhou | Early Cretaceous | A member of Enantiornithes, a relative of Pengornis. Type species P. eurycaudatus. |  | |||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Agnolin & Chafrat | Early Miocene | A member of Phorusrhacidae. Type species P. terrificus. | ||||
| Nom. nov | Valid | Zelenkov in Zelenkov & Kurochkin | Late Miocene | A member of Falconidae. A replacement name for Sushkinia Tugarinov (1935) (preoccupied). | ||||
| Sp. nov. | Valid | Boev | Early Pleistocene | |||||
| Sp. nov. | Valid | Tennyson, Cooper & Shepherd | Holocene | A member of Procellariidae, a species of gadfly petrel. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid [111] | Wang, Hu & Li | Early Cretaceous | A member of Enantiornithes. Type species P. dapingfangensis. | ||||
| Sp. nov. | Valid | Alcover et al. | Holocene | |||||
| Sp. nov. | Valid | Alcover et al. | Holocene | |||||
| Sp. nov. | Valid | Alcover et al. | Holocene |
| ||||
| Sp. nov. | Junior homonym | Alcover et al. | Holocene | A member of Rallidae, a species of Rallus. The specific name is a junior homonym of Rallus minutus Pallas (1776), Rallus minutus Gmelin (1789) and Rallus minutus Forster (1844). Alcover et al. (2016) coined a replacement name Rallus nanus.[113] | ||||
| Sp. nov. | Valid | Alcover et al. | Holocene | |||||
| Sp. nov. | Valid | Stucchi, Varas-Malca & Urbina-Schmitt | Miocene | A member of Sulidae, a species of Ramphastosula. | ||||
| Sp. nov. | Valid | Takano & Steadman | Late Holocene | A woodcock. | ||||
| Gen. nov. et Sp. nov. | Valid | Mourer-Chauviré, Pickford, & Senut | Middle Eocene | A Paraortygidae, Galliformes. Type species S. klinghardtensis. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Watanabe & Matsuoka | Pleistocene | A duck. The type species is Shiriyanetta hasegawai. | ||||
| Sp. nov. | Valid | Benson | Late Miocene |  | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Kaiser, Watanabe & Johns | Late Oligocene | A member of Plotopteridae. The type species is Stemec suntokum. |  | |||
| Sp. nov. | Valid | Stucchi, Varas-Malca & Urbina-Schmitt | Miocene | A booby. | ||||
| Sp. nov. | Valid | Stucchi, Varas-Malca & Urbina-Schmitt | Miocene | A booby. | ||||
| Sp. nov. | Valid | Quaternary (probably late Pleistocene) | ||||||
| Sp. nov | Valid | Pavia, Manegold, & Haarhoff | Early Pliocene | |||||
| Gen. et sp. nov. | Valid | Hu et al. | Early Cretaceous | A member of Enantiornithes. Type species Yuanjiawaornis viriosus. |
Pterosaurs
[edit]Research
[edit]- A study on the terrestrial locomotion of non-pterodactyloid pterosaurs is published by Witton (2015).[121]
- A specimen of Rhamphorhynchus muensteri with preserved soft tissues or impressions of soft tissues, stomach contents and possibly a coprolite is described by Hone et al. (2015).[122]
- Eleutério et al. (2015) study the bone microstructure characterization of two pterosaurs belonging to the group Anhangueria.[123]
- The paleoenvironments of azhdarchid pterosaurs from the Late Cretaceous of Kazakhstan are studied by Averianov et al. (2015).[124]
- Martill et al. (2015) describe a jaw bone attributed to the mid-Cretaceous pterosaur species Alanqa saharica from the Kem Kem beds of Morocco.[125]
New taxa
[edit]| Name | Novelty | Status | Authors | Age | Unit | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gen. et comb. nov | Valid | Kellner | Late Triassic (?Norian-Rhaetian) | A non-pterodactyloid pterosaur of uncertain phylogenetic placement; a new genus for "Eudimorphodon" cromptonellus Jenkins et al. (2001). | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Kellner | Late Triassic (late Norian) | A non-pterodactyloid pterosaur of uncertain phylogenetic placement. The type species is Austriadraco dallavecchiai. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Disputed | Headden & Campos | Early Cretaceous | Romualdo Formation | The type species is Banguela oberlii. Originally described as a dsungaripterid; Pêgas, Costa & Kellner (2018) considered the genus Banguela to be a junior synonym of the genus Thalassodromeus, and transferred the species B. oberlii to the latter genus.[128] | |||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Disputed | Kellner | Late Triassic (Alaunian) | Originally interpreted as a relative of Campylognathoides. The type species is Bergamodactylus wildi. Dalla Vecchia (2018) considers B. wildi to be a junior synonym of Carniadactylus rosenfeldi.[129] |  | |||
| Sp. nov | Valid | Myers | Late Cretaceous (late Cenomanian) | A member of Pterodactyloidea, probably a pteranodontoid; a species of Cimoliopterus. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Cheng et al. | Late Jurassic | A non-pterodactyloid pterosaur. The type species is Daohugoupterus delicatus. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Rodrigues et al. | Early Cretaceous (Aptian) | A member of Pteranodontoidea, possibly related to anhanguerians. The type species is Linlongopterus jennyae. | ||||
| Gen. et sp. nov | Valid | Lü et al. | Late Jurassic | A rhamphorhynchid. The type species is Orientognathus chaoyngensis. | ||||
| Sp. nov | Valid | O'Sullivan & Martill | Late Jurassic | Kimmeridge Clay Formation | A species of Rhamphorhynchus. |
References
[edit]- ^ Stephan Lautenschlager; Oliver W. M. Rauhut (2015). "Osteology of Rauisuchus tiradentes from the Late Triassic (Carnian) Santa Maria Formation of Brazil, and its implications for rauisuchid anatomy and phylogeny". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 173 (1): 55–91. doi:10.1111/zoj.12196.
- ^ Julia L. Molnar; Stephanie E. Pierce; Bhart-Anjan S. Bhullar; Alan H. Turner; John R. Hutchinson (2015). "Morphological and functional changes in the vertebral column with increasing aquatic adaptation in crocodylomorphs". Royal Society Open Science. 2 (11): 150439. Bibcode:2015RSOS....250439M. doi:10.1098/rsos.150439. PMC 4680616. PMID 26716001.
- ^ Mario Bronzati; Felipe C. Montefeltro; Max C. Langer (2015). "Diversification events and the effects of mass extinctions on Crocodyliformes evolutionary history". Royal Society Open Science. 2 (5): 140385. doi:10.1098/rsos.140385. PMC 4453258. PMID 26064649.
- ^ Philip D. Mannion; Roger B. J. Benson; Matthew T. Carrano; Jonathan P. Tennant; Jack Judd; Richard J. Butler (2015). "Climate constrains the evolutionary history and biodiversity of crocodylians". Nature Communications. 6: Article number 8438. Bibcode:2015NatCo...6.8438M. doi:10.1038/ncomms9438. PMC 4598718. PMID 26399170.
- ^ Eric W. Wilberg (2015). "What's in an Outgroup? The Impact of Outgroup Choice on the Phylogenetic Position of Thalattosuchia (Crocodylomorpha) and the Origin of Crocodyliformes". Systematic Biology. 64 (4): 621–637. doi:10.1093/sysbio/syv020. PMID 25840332.
- ^ Jeremy E. Martin; Peggy Vincent; Jocelyn Falconnet (2015). "The taxonomic content of Machimosaurus (Crocodylomorpha, Thalattosuchia)". Comptes Rendus Palevol. 14 (4): 305–310. doi:10.1016/j.crpv.2015.03.006.
- ^ Alfio A. Chiarenza; Davide Foffa; Mark T. Young; Gianni Insacco; Andrea Cau; Giorgio Carnevale; Rita Catanzariti (2015). "The youngest record of metriorhynchid crocodylomorphs, with implications for the extinction of Thalattosuchia". Cretaceous Research. 56: 608–616. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2015.07.001. hdl:2318/1537833.
- ^ Valentin Fischer; Maxim S. Arkhangelsky; Ilya M. Stenshin; Gleb N. Uspensky; Nikolay G. Zverkov; Roger B. J. Benson (2015). "Peculiar macrophagous adaptations in a new Cretaceous pliosaurid". Royal Society Open Science. 2 (12): 150552. Bibcode:2015RSOS....250552F. doi:10.1098/rsos.150552. PMC 4807462. PMID 27019740.
- ^ Xiao-Chun Wu; Donald B. Brinkman (2015). "A new crocodylian (Eusuchia) from the uppermost Cretaceous of Alberta, Canada". Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences. 52 (8): 590–607. Bibcode:2015CaJES..52..590W. doi:10.1139/cjes-2014-0133.
- ^ Alejandro Blanco; Josep Fortuny; Alba Vicente; Àngel H. Luján; Jordi Alexis García-Marçà; Albert G. Sellés (2015). "A new species of Allodaposuchus (Eusuchia, Crocodylia) from the Maastrichtian (Late Cretaceous) of Spain: phylogenetic and paleobiological implications". PeerJ. 3: e1171. doi:10.7717/peerj.1171. PMC 4558081. PMID 26339549.
- ^ a b c Rodolfo Salas-Gismondi; John J. Flynn; Patrice Baby; Julia V. Tejada-Lara; Frank P. Wesselingh; Pierre-Olivier Antoine (2015). "A Miocene hyperdiverse crocodylian community reveals peculiar trophic dynamics in proto-Amazonian mega-wetlands". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 282 (1804): 20142490. doi:10.1098/rspb.2014.2490. PMC 4375856. PMID 25716785.
- ^ Lindsay E. Zanno; Susan Drymala; Sterling J. Nesbitt; Vincent P. Schneider (2015). "Early crocodylomorph increases top tier predator diversity during rise of dinosaurs". Scientific Reports. 5: Article number 9276. Bibcode:2015NatSR...5E9276Z. doi:10.1038/srep09276. PMC 4365386. PMID 25787306.
- ^ Marcel B. Lacerda; Cesar L. Schultz; Cristina Bertoni-Machado (2015). "First 'Rauisuchian' archosaur (Pseudosuchia, Loricata) for the Middle Triassic Santacruzodon Assemblage Zone (Santa Maria Supersequence), Rio Grande do Sul State, Brazil". PLOS ONE. 10 (2): e0118563. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1018563L. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0118563. PMC 4340915. PMID 25714091.
- ^ Andrew B. Heckert; Vincent P. Schneider; Nicholas C. Fraser; Richard A. Webb (2015). "A new aetosaur (Archosauria, Suchia) from the Upper Triassic Pekin Formation, Deep River Basin, North Carolina, U.S.A., and its implications for early aetosaur evolution". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 35 (1): e881831. doi:10.1080/02724634.2014.881831. S2CID 140176110.
- ^ Steven C. Sweetman; Ulysse Pedreira-Segade; Steven Vidovic (2015). "A new bernissartiid crocodyliform from the Lower Cretaceous Wessex Formation (Wealden Group, Barremian) of the Isle of Wight, southern England". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 60 (2): 257–268. doi:10.4202/app.00038.2013.
- ^ Iván Narváez; Christopher A. Brochu; Fernando Escaso; Adán Pérez-García; Francisco Ortega (2015). "New Crocodyliforms from Southwestern Europe and Definition of a Diverse Clade of European Late Cretaceous Basal Eusuchians". PLOS ONE. 10 (11): e0140679. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1040679N. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0140679. PMC 4633049. PMID 26535893.
- ^ Eric W. Wilberg (2015). "A new metriorhynchoid (Crocodylomorpha, Thalattosuchia) from the Middle Jurassic of Oregon and the evolutionary timing of marine adaptations in thalattosuchian crocodylomorphs". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 35 (2): e902846. doi:10.1080/02724634.2014.902846. S2CID 83587692.
- ^ a b Emanuel Tschopp; Octávio Mateus; Roger B.J. Benson (2015). "A specimen-level phylogenetic analysis and taxonomic revision of Diplodocidae (Dinosauria, Sauropoda)". PeerJ. 3: e857. doi:10.7717/peerj.857. PMC 4393826. PMID 25870766.
- ^ Callaway, Ewen (2015). "Beloved Brontosaurus makes a comeback". Nature. doi:10.1038/nature.2015.17257. S2CID 163454894.
- ^ Federico Fanti; Andrea Cau; Luigi Cantelli; Mohsen Hassine; Marco Auditore (2015). "New Information on Tataouinea hannibalis from the Early Cretaceous of Tunisia and Implications for the Tempo and Mode of Rebbachisaurid Sauropod Evolution". PLOS ONE. 10 (4): e0123475. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1023475F. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0123475. PMC 4414570. PMID 25923211.
- ^ Karl T. Bates; Peter L. Falkingham; Sophie Macaulay; Charlotte Brassey; Susannah C. R. Maidment (2015). "Downsizing a giant: re-evaluating Dreadnoughtus body mass". Biology Letters. 11 (6): 20150215. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2015.0215. PMC 4528471. PMID 26063751.
- ^ Clint A. Boyd (2015). "The systematic relationships and biogeographic history of ornithischian dinosaurs". PeerJ. 3: e1523. doi:10.7717/peerj.1523. PMC 4690359. PMID 26713260.
- ^ Kenneth Carpenter; Matthew C. Lamanna (2015). "The braincase assigned to the ornithopod dinosaur Uteodon McDonald, 2011, reassigned to Dryosaurus Marsh, 1894: implications for iguanodontian morphology and taxonomy". Annals of Carnegie Museum. 83 (2): 149–165. doi:10.2992/007.083.0201. S2CID 85612127.
- ^ Albert Prieto-Márquez; Jonathan R. Wagner; Phil R. Bell; Luis M. Chiappe (2015). "The late-surviving 'duck-billed' dinosaur Augustynolophus from the upper Maastrichtian of western North America and crest evolution in Saurolophini". Geological Magazine. 152 (2): 225–241. Bibcode:2015GeoM..152..225P. doi:10.1017/S0016756814000284. S2CID 131049979.
- ^ Phil R. Bell; Philip J. Currie (2015). "A high-latitude dromaeosaurid, Boreonykus certekorum, gen. et sp. nov. (Theropoda), from the upper Campanian Wapiti Formation, west-central Alberta". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 36 (1): e1034359. doi:10.1080/02724634.2015.1034359. S2CID 131680329.
- ^ Fernando E. Novas; Leonardo Salgado; Manuel Suárez; Federico L. Agnolín; Martín D. Ezcurra; Nicolás R. Chimento; Rita de la Cruz; Marcelo P. Isasi; Alexander O. Vargas; David Rubilar-Rogers (2015). "An enigmatic plant-eating theropod from the Late Jurassic period of Chile". Nature. 522 (7556): 331–334. Bibcode:2015Natur.522..331N. doi:10.1038/nature14307. PMID 25915021. S2CID 4407531.
- ^ Matthew G. Baron; Paul M. Barrett (2017). "A dinosaur missing-link? Chilesaurus and the early evolution of ornithischian dinosaurs". Biology Letters. 13 (8): 20170220. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2017.0220. PMC 5582101. PMID 28814574.
- ^ Victoria M. Arbour; Philip J. Currie (2015). "Systematics, phylogeny and palaeobiogeography of the ankylosaurid dinosaurs". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 14 (5): 385–444. doi:10.1080/14772019.2015.1059985. S2CID 214625754.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2019-12-05. Retrieved 2015-07-29.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Robert A. DePalma; David A. Burnham; Larry D. Martin; Peter L. Larson; Robert T. Bakker (2015). "The first giant raptor (Theropoda: Dromaeosauridae) from the Hell Creek Formation". Paleontological Contributions. 14: 1–16. hdl:1808/18764.
- ^ Blair W. McPhee; Jonah N. Choiniere; Adam M. Yates; Pia A. Viglietti (2015). "A second species of Eucnemesaurus Van Hoepen, 1920 (Dinosauria, Sauropodomorpha): new information on the diversity and evolution of the sauropodomorph fauna of South Africa's lower Elliot Formation (latest Triassic)". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 35 (5): e980504. doi:10.1080/02724634.2015.980504. S2CID 86805607.
- ^ Malkani, M.S., 2015. Dinosaurs, Mesoeucrocodiles, Pterosaurs, New Fauna and Flora from Pakistan. Geological Survey of Pakistan, Information Release 823: 1-32.
- ^ Paul Upchurch; Philip D. Mannion; Michael P. Taylor (2015). "The Anatomy and Phylogenetic Relationships of "Pelorosaurus" becklesii (Neosauropoda, Macronaria) from the Early Cretaceous of England". PLOS ONE. 10 (6): e0125819. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1025819U. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0125819. PMC 4454574. PMID 26039587.
- ^ William T. Blows (2015). British Polacanthid Dinosaurs: Observations on the History and Palaeontology of the UK Polacanthid Armoured Dinosaurs and Their Relatives. Siri Scientific Press. pp. 1–224. ISBN 9780992997946.
- ^ Fenglu Han; Catherine A. Forster; James M. Clark; Xing Xu (2015). "A New Taxon of Basal Ceratopsian from China and the Early Evolution of Ceratopsia". PLOS ONE. 10 (12): e0143369. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1043369H. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0143369. PMC 4674058. PMID 26649770.
- ^ Junchang Lü; Hanyong Pu; Yoshitsugu Kobayashi; Li Xu; Huali Chang; Yuhua Shang; Di Liu; Yuong-Nam Lee; Martin Kundrát; Caizhi Shen (2015). "A New Oviraptorid Dinosaur (Dinosauria: Oviraptorosauria) from the Late Cretaceous of Southern China and Its Paleobiogeographical Implications". Scientific Reports. 5: Article number 11490. Bibcode:2015NatSR...511490L. doi:10.1038/srep11490. PMC 4489096. PMID 26133245.
- ^ Francisco J. Verdú; Rafael Royo-Torres; Alberto Cobos; Luis Alcalá (2015). "Perinates of a new species of Iguanodon (Ornithischia: Ornithopoda) from the lower Barremian of Galve (Teruel, Spain)". Cretaceous Research. 56: 250–264. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2015.05.010.
- ^ Yiming He; Peter J. Makovicky; Kebai Wang; Shuqing Chen; Corwin Sullivan; Fenglu Han; Xing Xu (2015). "A new leptoceratopsid (Ornithischia, Ceratopsia) with a unique ischium from the Upper Cretaceous of Shandong Province, China". PLOS ONE. 10 (12): e0144148. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1044148H. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0144148. PMC 4689537. PMID 26701114.
- ^ Masateru Shibata; Yoichi Azuma (2015). "New basal hadrosauroid (Dinosauria: Ornithopoda) from the Lower Cretaceous Kitadani Formation, Fukui, central Japan". Zootaxa. 3914 (4): 421–440. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3914.4.3. PMID 25661952.
- ^ Lucy G. Leahey; Ralph E. Molnar; Kenneth Carpenter; Lawrence M. Witmer; Steven W. Salisbury (2015). "Cranial osteology of the ankylosaurian dinosaur formerly known as Minmi sp. (Ornithischia: Thyreophora) from the Lower Cretaceous Allaru Mudstone of Richmond, Queensland, Australia". PeerJ. 3: e1475. doi:10.7717/peerj.1475. PMC 4675105. PMID 26664806.
- ^ a b V. R. Alifanov; S. V. Saveliev (2015). "The Most Ancient Ornithomimosaur (Theropoda, Dinosauria), with Cover Imprints from the Upper Jurassic of Russia". Paleontological Journal. 49 (6): 636–650. doi:10.1134/S0031030115060039. S2CID 131199807.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Andrea Cau (November 24, 2015). "Cosa è Lepidocheirosaurus?". Theropoda. Retrieved November 25, 2015.
- ^ Pascal Godefroit; Sofia M. Sinitsa; Aude Cincotta; Maria E. McNamara; Svetlana A. Reshetova; Danielle Dhouailly (2020). "Integumentary structures in Kulindadromeus zabaikalicus, a basal neornithischian dinosaur from the Jurassic of Siberia". In Christian Foth; Oliver W. M. Rauhut (eds.). The evolution of feathers. Fascinating Life Sciences. Springer. pp. 47–62. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-27223-4_4. ISBN 978-3-030-27223-4. S2CID 216261986.
- ^ Sterling J. Nesbitt; Martín D. Ezcurra (2015). "The early fossil record of dinosaurs in North America: A new neotheropod from the base of the Upper Triassic Dockum Group of Texas". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 60 (3): 513–526. doi:10.4202/app.00143.2014.
- ^ José Miguel Gasulla; Fernando Escaso; Iván Narváez; Francisco Ortega; José Luis Sanz (2015). "A New Sail-Backed Styracosternan (Dinosauria: Ornithopoda) from the Early Cretaceous of Morella, Spain". PLOS ONE. 10 (12): e0144167. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1044167G. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0144167. PMC 4691198. PMID 26673161.
- ^ Wenjie Zheng; Xingsheng Jin; Xing Xu (2015). "A psittacosaurid-like basal neoceratopsian from the Upper Cretaceous of central China and its implications for basal ceratopsian evolution". Scientific Reports. 5: Article number 14190. Bibcode:2015NatSR...514190Z. doi:10.1038/srep14190. PMC 4585677. PMID 26388024.
- ^ Lida Xing; Tetsuto Miyashita; Philip J. Currie; Hailu You; Zhiming Dong (2015). "A new basal eusauropod from the Middle Jurassic of Yunnan, China, and faunal compositions and transitions of Asian sauropodomorph dinosaurs". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 60 (1): 145–154. doi:10.4202/app.2012.0151.
- ^ José L. Carballido; Diego Pol; Mary L. Parra Ruge; Santiago Padilla Bernal; María E. Páramo-Fonseca; Fernando Etayo-Serna (2015). "A new Early Cretaceous brachiosaurid (Dinosauria, Neosauropoda) from northwestern Gondwana (Villa de Leiva, Colombia)". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 35 (5): e980505. doi:10.1080/02724634.2015.980505. S2CID 129498917.
- ^ Elizabeth A. Freedman Fowler; John R. Horner (2015). "A New Brachylophosaurin Hadrosaur (Dinosauria: Ornithischia) with an Intermediate Nasal Crest from the Campanian Judith River Formation of Northcentral Montana". PLOS ONE. 10 (11): e0141304. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1041304F. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0141304. PMC 4641681. PMID 26560175.
- ^ Blair W. McPhee; Matthew F. Bonnan; Adam M. Yates; Johann Neveling; Jonah N. Choiniere (2015). "A new basal sauropod from the pre-Toarcian Jurassic of South Africa: evidence of niche-partitioning at the sauropodomorph–sauropod boundary?". Scientific Reports. 5: Article number 13224. Bibcode:2015NatSR...513224M. doi:10.1038/srep13224. PMC 4541066. PMID 26288028.
- ^ Lida Xing; Tetsuto Miyashita; Jianping Zhang; Daqing Li; Yong Ye; Toru Sekiya; Fengping Wang; Philip J. Currie (2015). "A new sauropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic of China and the diversity, distribution, and relationships of mamenchisaurids". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 35 (1): e889701. doi:10.1080/02724634.2014.889701. S2CID 86062974.
- ^ Caleb M. Brown; Donald M. Henderson (2015). "A New Horned Dinosaur Reveals Convergent Evolution in Cranial Ornamentation in Ceratopsidae". Current Biology. 25 (12): 1641–1648. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2015.04.041. PMID 26051892.
- ^ Steven E. Jasinski (2015). "A new dromaeosaurid (Theropoda: Dromaeosauridae) from the Late Cretaceous of New Mexico". New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin. 67: 79–88.
- ^ Alejandro Otero; Emil Krupandan; Diego Pol; Anusuya Chinsamy; Jonah Choiniere (2015). "A new basal sauropodiform from South Africa and the phylogenetic relationships of basal sauropodomorphs". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 174 (3): 589–634. doi:10.1111/zoj.12247. hdl:11336/38019.
- ^ Masateru Shibata; Pratueng Jintasakul; Yoichi Azuma; Hai-Lu You (2015). "A New Basal Hadrosauroid Dinosaur from the Lower Cretaceous Khok Kruat Formation in Nakhon Ratchasima Province, Northeastern Thailand". PLOS ONE. 10 (12): e0145904. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1045904S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0145904. PMC 4696827. PMID 26716981.
- ^ Hirotsugu Mori; Patrick S. Druckenmiller; Gregory M. Erickson (2015). "A new Arctic hadrosaurid from the Prince Creek Formation (lower Maastrichtian) of northern Alaska". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 61 (1): 15–32. doi:10.4202/app.00152.2015.
- ^ Ryuji Takasaki; Anthony R. Fiorillo; Ronald S. Tykoski; Yoshitsugu Kobayashi (2020). "Re-examination of the cranial osteology of the Arctic Alaskan hadrosaurine with implications for its taxonomic status". PLOS ONE. 15 (5): e0232410. Bibcode:2020PLoSO..1532410T. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0232410. PMC 7202651. PMID 32374777.
- ^ David C. Evans; Michael J. Ryan (2015). "Cranial Anatomy of Wendiceratops pinhornensis gen. et sp. nov., a Centrosaurine Ceratopsid (Dinosauria: Ornithischia) from the Oldman Formation (Campanian), Alberta, Canada, and the Evolution of Ceratopsid Nasal Ornamentation". PLOS ONE. 10 (7): e0130007. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1030007E. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0130007. PMC 4496092. PMID 26154293.
- ^ Xing Xu; Xiaoting Zheng; Corwin Sullivan; Xiaoli Wang; Lida Xing; Yan Wang; Xiaomei Zhang; Jingmai K. O’Connor; Fucheng Zhang; Yanhong Pan (2015). "A bizarre Jurassic maniraptoran theropod with preserved evidence of membranous wings". Nature. 521 (7550): 70–73. Bibcode:2015Natur.521...70X. doi:10.1038/nature14423. PMID 25924069. S2CID 205243599.
- ^ Junchang Lü; Stephen L. Brusatte (2015). "A large, short-armed, winged dromaeosaurid (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Early Cretaceous of China and its implications for feather evolution". Scientific Reports. 5: Article number 11775. Bibcode:2015NatSR...511775L. doi:10.1038/srep11775. PMC 4504142. PMID 26181289.
- ^ Andrea Cau; Tom Brougham; Darren Naish (2015). "The phylogenetic affinities of the bizarre Late Cretaceous Romanian theropod Balaur bondoc (Dinosauria, Maniraptora): dromaeosaurid or flightless bird?". PeerJ. 3: e1032. doi:10.7717/peerj.1032. PMC 4476167. PMID 26157616.
- ^ Murray Williams (2015). "Size and flight capability of Anas chathamica, an extinct duck from Chatham Island, New Zealand". Wildfowl. 65: 75–99.
- ^ Chris R. Torres; Vanesa L. De Pietri; Antoine Louchart; Marcel van Tuinen (2015). "New cranial material of the earliest filter-feeding flamingo Harrisonavis croizeti (Aves, Phoenicopteridae) informs the evolution of the highly specialized filter feeding apparatus". Organisms Diversity & Evolution. 15 (3): 609–618. doi:10.1007/s13127-015-0209-7. S2CID 18198929.
- ^ Gerald Mayr (2015). "Skeletal morphology of the middle Eocene swift Scaniacypselus and the evolutionary history of true swifts (Apodidae)". Journal of Ornithology. 156 (2): 441–450. doi:10.1007/s10336-014-1142-9. S2CID 14282557.
- ^ Gerald Mayr (2015). "A new specimen of the Early Eocene Masillacolius brevidactylus and its implications for the evolution of feeding specializations in mousebirds (Coliiformes)". Comptes Rendus Palevol. 14 (5): 363–370. doi:10.1016/j.crpv.2015.05.007.
- ^ Gerald Mayr (2015). "A reassessment of Eocene parrotlike fossils indicates a previously undetected radiation of zygodactyl stem group representatives of passerines (Passeriformes)". Zoologica Scripta. 44 (6): 587–602. doi:10.1111/zsc.12128. S2CID 85599482.
- ^ Storrs L. Olson (2015). "History, morphology, and fossil record of the extinct Puerto Rican Parakeet Psittacara maugei Souancé". The Wilson Journal of Ornithology. 127 (1): 1–12. doi:10.1676/14-020.1. S2CID 84512973.
- ^ Xavier La Canna (2015). "New species of dwarf emu discovered from fossils at Alcoota in Central Australia". ABC News.
- ^ Washington W. Jones; Marcos M. Cenizo; Federico L. Agnolin; Andrés Rinderknecht; R. Ernesto Blanco (2015). "The largest known falconid". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen. 277 (3): 361–372. doi:10.1127/njgpa/2015/0514.
- ^ Leon P. A. M. Claessens; Hanneke J. M. Meijer; Julian P. Hume (2015). "The Morphology of the Thirioux dodos". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 35 (Supplement 1): 29–187. doi:10.1080/02724634.2015.1121723. S2CID 87957947.
- ^ Albrecht Manegold; Nikita Zelenkov (2015). "A new species of Aegypius vulture from the early Pliocene of Moldova is the earliest unequivocal evidence of Aegypiinae in Europe". Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 89 (3): 529–534. doi:10.1007/s12542-014-0242-4. S2CID 129035036.
- ^ Joseph Michael Forshaw (2015). Pigeons and doves in Australia. CSIRO Publishing. pp. 84–85. ISBN 9780643096332.
- ^ International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (2010). "OPINION 2251 (Case 3442) Columba norfolciensis Latham, 1801 (Aves, COLUMBIDAE): name suppressed". Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature. 67 (2): 192–193. doi:10.21805/bzn.v67i2.a15. S2CID 193143627.
- ^ a b Nikita V. Zelenkov; Andrey V. Panteleyev (2015). "Three bird taxa (Aves: Anatidae, Phasianidae, Scolopacidae) from the Late Miocene of the Sea of Azov (Southwestern Russia)". Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 89 (3): 515–527. doi:10.1007/s12542-014-0238-0. S2CID 85276099.
- ^ Min Wang; Xiaoting Zheng; Jingmai K. O’Connor; Graeme T. Lloyd; Xiaoli Wang; Yan Wang; Xiaomei Zhang; Zhonghe Zhou (2015). "The oldest record of Ornithuromorpha from the Early Cretaceous of China". Nature Communications. 6: Article number 6987. Bibcode:2015NatCo...6.6987W. doi:10.1038/ncomms7987. PMC 5426517. PMID 25942493.
- ^ a b Marco Pavia; Albrecht Manegold; Pippa Haarhoff (2015). "Early Pliocene owls from Langebaanweg, South Africa, with first evidence of the genus Athene south of the Sahara and the description of a new species of Tyto". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 60 (4): 815–828. doi:10.4202/app.00077.2014.
- ^ Zlatozar Boev (2015). "An Early Pleistocene Snake Eagle, Circaetus haemusensis sp. n. (Aves, Accipitriformes) from Varshets, Northwestern Bulgaria" (PDF). Acta Zoologica Bulgarica. 67 (1): 127–138.
- ^ a b Ismar Carvalho; Fernando E. Novas; Federico L. Agnolín; Marcelo P. Isasi; Francisco I. Freitas; José A. Andrade (2015). "A new genus and species of enantiornithine bird from the Early Cretaceous of Brazil". Brazilian Journal of Geology. 45 (2): 161–171. doi:10.1590/23174889201500020001.
- ^ Ismar de Souza Carvalho; Fernando E. Novas; Federico L. Agnolín; Marcelo P. Isasi; Francisco I. Freitas; José A. Andrade (2015). "A Mesozoic bird from Gondwana preserving feathers". Nature Communications. 6: Article number 7141. Bibcode:2015NatCo...6.7141D. doi:10.1038/ncomms8141. PMC 4458891. PMID 26035285.
- ^ Min Wang; Daqing Li; Jingmai K. O'Connor; Zhonghe Zhou; Hailu You (2015). "Second species of enantiornithine bird from the Lower Cretaceous Changma Basin, northwestern China with implications for the taxonomic diversity of the Changma avifauna". Cretaceous Research. 55: 56–65. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2015.01.008.
- ^ Gerald Mayr (2015). "Towards completion of the early Eocene aviary: A new bird group from the Messel oil shale (Aves, Eopachypterygidae, fam. nov.)". Zootaxa. 4013 (2): 252–264. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4013.2.6. PMID 26623896. S2CID 10270683.
- ^ Jingmai K. O’Connor; Da-Qing Li; Matthew C. Lamanna; Min Wang; Jerald D. Harris; Jessie Atterholt; Hai-Lu You (2015). "A new Early Cretaceous enantiornithine (Aves, Ornithothoraces) from northwestern China with elaborate tail ornamentation". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 36 (1): e1054035. doi:10.1080/02724634.2015.1054035. S2CID 85800831.
- ^ Tao Zhao; Gerald Mayr; Min Wang; Wei Wang (2015). "A trogon-like arboreal bird from the early Eocene of China". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology. 39 (2): 287–294. doi:10.1080/03115518.2015.994160. S2CID 131668423.
- ^ Alyssa Bell; Luis M. Chiappe (2015). "Identification of a New Hesperornithiform from the Cretaceous Niobrara Chalk and Implications for Ecologic Diversity among Early Diving Birds". PLOS ONE. 10 (11): e0141690. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1041690B. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0141690. PMC 4651437. PMID 26580402.
- ^ Vanesa L. De Pietri; R. Paul Scofield; Alan J. D. Tennyson; Suzanne J. Hand; Trevor H. Worthy (2015). "Wading a lost southern connection: Miocene fossils from New Zealand reveal a new lineage of shorebirds (Charadriiformes) linking Gondwanan avifaunas". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 14 (7): 603–616. doi:10.1080/14772019.2015.1087064. hdl:2328/35949. S2CID 85816940.
- ^ http://zoobank.org/References/B0DFB37D-1BA4-42D2-87B2-47F3B7CCF9C4 [dead link]
- ^ Nikita V. Zelenkov; Alexander O. Averianov (2015). "A historical specimen of enantiornithine bird from the Early Cretaceous of Mongolia representing a new taxon with a specialized neck morphology". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 14 (4): 319–338. doi:10.1080/14772019.2015.1051146. S2CID 85784633.
- ^ http://zoobank.org/References/42845FFC-4E4B-4FEE-9D76-0B5A7D9E127B [dead link]
- ^ Min Wang; Di Liu (2015). "Taxonomical reappraisal of Cathayornithidae (Aves: Enantiornithes)". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 14 (1): 29–47. doi:10.1080/14772019.2014.994087. S2CID 86665059.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2019-08-15. Retrieved 2015-01-19.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Hume, Julian P. (2015). "A new subfossil bulbul (Aves: Passerines: Pycnonotidae) from Rodrigues Island, Mascarenes, south-western Indian Ocean". Ostrich: Journal of African Ornithology. 86 (3): 247–260. doi:10.2989/00306525.2015.1067651. S2CID 83835055.
- ^ http://zoobank.org/References/D979AC29-B662-4A39-B4CA-984E04EB6B65 [dead link]
- ^ Ren-fei Wang; Yan Wang; Dong-yu Hu (2015). "Discovery of a new ornithuromorph genus, Juehuaornis gen.nov. from Lower Cretaceous of western Liaoning, China". Global Geology. 34 (1): 7–11. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2015.01.002.
- ^ Marcelo Stucchi; Steven D. Emslie; Rafael M. Varas-Malca; Mario Urbina-Schmitt (2015). "A new late Miocene condor (Aves, Cathartidae) from Peru and the origin of South American condors". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 35 (5): e972507. doi:10.1080/02724634.2015.972507. S2CID 128790925.
- ^ Thomas A. Stidham; Richard P. Hilton (2015). "New data on stiff-tailed duck evolution and dispersal from a new species of diving duck (Anseriformes: Anatidae: cf. Oxyurinae) from the Miocene High Rock Caldera in north-west Nevada, USA". Papers in Palaeontology. 2 (1): 41–58. doi:10.1002/spp2.1029. S2CID 85776578.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2020-03-18. Retrieved 2015-10-10.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Federico J. Degrange; Claudia P. Tambussi; Matías L. Taglioretti; Alejandro Dondas; Fernando Scaglia (2015). "A new Mesembriornithinae (Aves, Phorusrhacidae) provides new insights into the phylogeny and sensory capabilities of terror birds". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 35 (2): e912656. doi:10.1080/02724634.2014.912656. hdl:11336/38650. S2CID 85212917.
- ^ Gerald Mayr (2015). "A new Paleogene procellariiform bird from western North America". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen. 275 (1): 11–17. doi:10.1127/njgpa/2015/0445.
- ^ Evgeniy A. Zvonok; Nikita V. Zelenkov; Igor G. Danilov (2015). "A new unusual waterbird (Aves, ?Suliformes) from the Eocene of Kazakhstan". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 36 (1): e1035783. doi:10.1080/02724634.2015.1035783. S2CID 87129911.
- ^ Nikita V. Zelenkov (2015). "A Primitive Grebe (Aves, Podicipedidae) from the Miocene of Eastern Siberia (Lake Baikal, Olkhon Island)". Paleontological Journal. 49 (5): 521–529. doi:10.1134/S0031030115050159. S2CID 130057204. Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2015-10-03.
- ^ a b Nikita V. Zelenkov; Evgeny N. Kurochkin (2015). "КЛАСС AVES". In E.N. Kurochkin; A.V. Lopatin; N.V. Zelenkov (eds.). Ископаемые позвоночные России и сопредельных стран. Ископаемые рептилии и птицы. Часть 3 / Fossil vertebrates of Russia and adjacent countries. Fossil Reptiles and Birds. Part 3. GEOS. pp. 86–290. ISBN 978-5-89118-699-6.
- ^ Trevor H. Worthy; Stuart Hawkins; Stuart Bedford; Matthew Spriggs (2015). "Avifauna from the Teouma Lapita Site, Efate Island, Vanuatu, including a New Genus and Species of Megapode". Pacific Science. 69 (2): 205–254. doi:10.2984/69.2.6. hdl:2328/35948. S2CID 83687153.
- ^ a b Cécile Mourer-Chauviré; Martin Pickford; Brigitte Senut (2015). "Stem group galliform and stem group psittaciform birds (Aves, Galliformes, Paraortygidae, and Psittaciformes, family incertae sedis) from the Middle Eocene of Namibia". Journal of Ornithology. 156 (1): 275–286. doi:10.1007/s10336-014-1124-y. S2CID 16336177.
- ^ Andrzej Elżanowski; Nikita V. Zelenkov (2015). "A primitive heron (Aves: Ardeidae) from the Miocene of Central Asia". Journal of Ornithology. 156 (3): 837–846. doi:10.1007/s10336-015-1164-y.
- ^ Vanesa L. De Pietri; Aaron B. Camens; Trevor H. Worthy (2015). "A Plains-wanderer (Pedionomidae) that did not wander plains: a new species from the Oligocene of South Australia". Ibis. 157 (1): 68–74. doi:10.1111/ibi.12215. hdl:2328/35950.
- ^ a b Federico L. Agnolin; Pablo Chafrat (2015). "New fossil bird remains from the Chichinales Formation (Early Miocene) of northern Patagonia, Argentina". Annales de Paléontologie. 101 (2): 87–94. doi:10.1016/j.annpal.2015.02.001.
- ^ Han Hu; Jingmai K. O’Connor; Zhonghe Zhou (2015). "A New Species of Pengornithidae (Aves: Enantiornithes) from the Lower Cretaceous of China Suggests a Specialized Scansorial Habitat Previously Unknown in Early Birds". PLOS ONE. 10 (6): e0126791. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1026791H. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0126791. PMC 4454694. PMID 26039693.
- ^ Zlatozar Boev (2015). "Porzana botunensis sp. n., a New Early Pleistocene Crake (Aves: Rallidae) from Bulgaria" (PDF). Acta Zoologica Bulgarica. 67 (2): 283–290.
- ^ Alan J. D. Tennyson; Joanne H. Cooper; Lara D. Shepherd (2015). "A new species of extinct Pterodroma petrel (Procellariiformes: Procellariidae) from the Chatham Islands, New Zealand". Bulletin of the British Ornithologists' Club. 135 (3): 267–277.
- ^ Min Wang; Han Hu; Zhiheng Li (2015). "A new small enantiornithine bird from the Jehol Biota, with implications for early evolution of avian skull morphology". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 14 (6): 481–497. doi:10.1080/14772019.2015.1073801. S2CID 83603202.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2019-08-18. Retrieved 2015-08-22.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ a b c d e Josep Antoni Alcover; Harald Pieper; Fernando Pereira; Juan Carlos Rando (2015). "Five new extinct species of rails (Aves: Gruiformes: Rallidae) from the Macaronesian Islands (North Atlantic Ocean)". Zootaxa. 4057 (2): 151–190. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4057.2.1. hdl:10261/132286. PMID 26701473.
- ^ Josep Antoni Alcover; Harald Pieper; Fernando Pereira; Juan Carlos Rando (2016). "Rallus nanus nomen novum: a replacement name for Rallus minutus Alcover et al. 2015". Zootaxa. 4085 (1): 141–142. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4085.1.8. hdl:10261/133112. PMID 27394294.
- ^ a b c Marcelo Stucchi; Rafael M. Varas-Malca; Mario Urbina-Schmitt (2015). "New Miocene sulid birds from Peru and considerations on their Neogene fossil record in the Eastern Pacific Ocean". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 61 (2): 417–427. doi:10.4202/app.00170.2015.
- ^ Oona M. Takano; David W. Steadman (2015). "A new species of Woodcock (Aves: Scolopacidae: Scolopax) from Hispaniola, West Indies". Zootaxa. 4032 (1): 117–126. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4032.1.6. PMID 26624342. S2CID 44325093.
- ^ Junya Watanabe; Hiroshige Matsuoka (2015). "Flightless diving duck (Aves, Anatidae) from the Pleistocene of Shiriya, Northeast Japan". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 35 (6): e994745. doi:10.1080/02724634.2014.994745. S2CID 83689129.
- ^ Richard D. Benson (2015). "A new species of penguin from the late Miocene of Chile, with comments on the stratigraphic range of Palaeospheniscus" (PDF). Scientific Publications of the Science Museum of Minnesota. New Series. 8 (4): 5–22.
- ^ Gary Kaiser; Junya Watanabe; Marji Johns (2015). "A new member of the family Plotopteridae (Aves) from the late Oligocene of British Columbia, Canada". Palaeontologia Electronica. 18 (3): Article number 18.3.52A. doi:10.26879/563.
- ^ William Suárez; Storrs L. Olson (2015). "Systematics and distribution of the giant fossil barn owls of the West Indies (Aves: Strigiformes: Tytonidae)". Zootaxa. 4020 (3): 533–553. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4020.3.7. PMID 26624114.
- ^ Dongyu Hu; Ying Liu; Jinhua Li; Xing Xu; Lianhai Hou (2015). "Yuanjiawaornis viriosus, gen. et sp. nov., a large enantiornithine bird from the Lower Cretaceous of western Liaoning, China". Cretaceous Research. 55: 210–219. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2015.02.013.
- ^ Mark P. Witton (2015). "Were early pterosaurs inept terrestrial locomotors?". PeerJ. 3: e1018. doi:10.7717/peerj.1018. PMC 4476129. PMID 26157605.
- ^ David Hone; Donald M. Henderson; François Therrien; Michael B. Habib (2015). "A specimen of Rhamphorhynchus with soft tissue preservation, stomach contents and a putative coprolite". PeerJ. 3: e1191. doi:10.7717/peerj.1191. PMC 4548500. PMID 26312182.
- ^ Eleutério, L. H.; Bantim, R. A. M.; Lima, F. J.; Pedroso de Andrade, R. C. L.; Saraiva, A. A. F.; Kellner, A. W. A.; Sayao, J. M. (2015). "Biomechanical and physiological influences on the osteohistological deposition of Anhangueria (Pterosauria, Pterodactyloidea)" (PDF). Revista Brasileira de Paleontologia. 18 (3): 403–412. doi:10.4072/rbp.2015.3.06.
- ^ Averianov, A. O.; Dyke, G. J.; Danilov, I. G.; Skutschas, P. P. (2015). "The paleoenvironments of azhdarchid pterosaurs localities in the Late Cretaceous of Kazakhstan". ZooKeys (483): 59–80. doi:10.3897/zookeys.483.9058. PMC 4351447. PMID 25755624.
- ^ Martill, D.M.; Ibrahim, N. (2015). "An unusual modification of the jaws in cf. Alanqa, a mid-Cretaceous azhdarchid pterosaur from the Kem Kem beds of Morocco" (PDF). Cretaceous Research. 53: 59–67. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2014.11.001.
- ^ a b c Alexander W.A. Kellner (2015). "Comments on Triassic pterosaurs with discussion about ontogeny and description of new taxa". Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências. 87 (2): 669–689. doi:10.1590/0001-3765201520150307. PMID 26131631.
- ^ Jaime A. Headden; Hebert B.N. Campos (2015). "An unusual edentulous pterosaur from the Early Cretaceous Romualdo Formation of Brazil". Historical Biology: An International Journal of Paleobiology. 27 (7): 815–826. doi:10.1080/08912963.2014.904302. S2CID 129306469.
- ^ Rodrigo V. Pêgas; Fabiana R. Costa; Alexander W.A. Kellner (2018). "New information on the osteology and a taxonomic revision of the genus Thalassodromeus (Pterodactyloidea, Tapejaridae, Thalassodrominae)". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 38 (2): e1443273. doi:10.1080/02724634.2018.1443273. S2CID 90477315.
- ^ Fabio M. Dalla Vecchia (2018). "Comments on Triassic pterosaurs with a commentary on the "ontogenetic stages" of Kellner (2015) and the validity of Bergamodactylus wildi". Rivista Italiana di Paleontologia e Stratigrafia. 124 (2): 317–341. doi:10.13130/2039-4942/10099.
- ^ Timothy S. Myers (2015). "First North American occurrence of the toothed pteranodontoid pterosaur Cimoliopterus". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 35 (6): e1014904. doi:10.1080/02724634.2015.1014904. S2CID 86099117.
- ^ Xin Cheng; Xiaolin Wang; Shunxing Jiang; Alexander W.A. Kellner (2015). "Short note on a non-pterodactyloid pterosaur from Upper Jurassic deposits of Inner Mongolia, China". Historical Biology: An International Journal of Paleobiology. 27 (6): 749–754. doi:10.1080/08912963.2014.974038. S2CID 128454476.
- ^ Taissa Rodrigues; Shunxing Jiang; Xin Cheng; Xiaolin Wang; Alexander W.A. Kellner (2015). "A new toothed pteranodontoid (Pterosauria, Pterodactyloidea) from the Jiufotang Formation (Lower Cretaceous, Aptian) of China and comments on Liaoningopterus gui Wang and Zhou, 2003". Historical Biology: An International Journal of Paleobiology. 27 (6): 782–795. doi:10.1080/08912963.2015.1033417. S2CID 129062416.
- ^ Junchang Lü; Hanyong Pu; Li Xu; Xuefang Wei; Huali Chang; Martin Kundrát (2015). "A new rhamphorhynchid pterosaur (Pterosauria) from Jurassic deposits of Liaoning Province, China". Zootaxa. 3911 (1): 119–129. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3911.1.7. PMID 25661600.
- ^ Michael O'Sullivan; David M. Martill (2015). "Evidence for the presence of Rhamphorhynchus (Pterosauria: Rhamphorhynchinae) in the Kimmeridge Clay of the UK" (PDF). Proceedings of the Geologists' Association. 126 (3): 390–401. doi:10.1016/j.pgeola.2015.03.003.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch