Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics - Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics, (NUTS) for the French nomenclature d'unités territoriales statistiques, is a geocode standard that shows the administrative divisions of countries for statistical purposes. It was made by the European Union, so it only covers the member states of that union in detail.
A NUTS code begins with a two-letter code referencing the country, and is identical to the ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 code (the only difference is UK instead of GB for the United Kingdom). The subdivision of the country is then displayed by one number. A second or third subdivision level is referred to with another number each. Each numbering starts with 1, as 0 is used for the upper level. In case the subdivision has more than 9 entities, capital letters are used to continue the numbering.
In addition to the full three levels for the European Union countries, all countries have a NUTS code with a two-letter code for a continent and two numbers for the country, and for the USA, Canada and Australia the states, provinces, and territories are numbered separately.
Some are not easily classified: for example, Gibraltar is listed as being outside the EU with the code EO21; while French Guiana is listed twice, once in France as FR930 and once in South America as AS13.
NUTS, in some ways are similar to the ISO 3166-2 standard, as well as the FIPS standard of the United States.
Levels
[change | change source]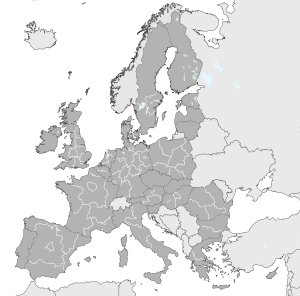

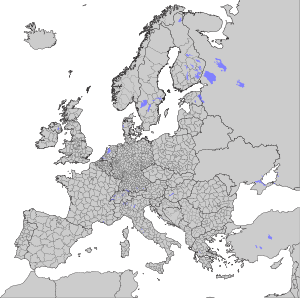
There are three levels of NUTS. Some with two levels of local administrative units (LAUs) below. These were called NUTS levels 4 and 5 until July 2003, but were changed due to official regulations although they are sometimes still described as such. Note that not all countries have every level of division, depending on their size. One of the most extreme cases is Luxembourg, which has only LAUs; the three NUTS divisions each correspond to the entire country itself.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch